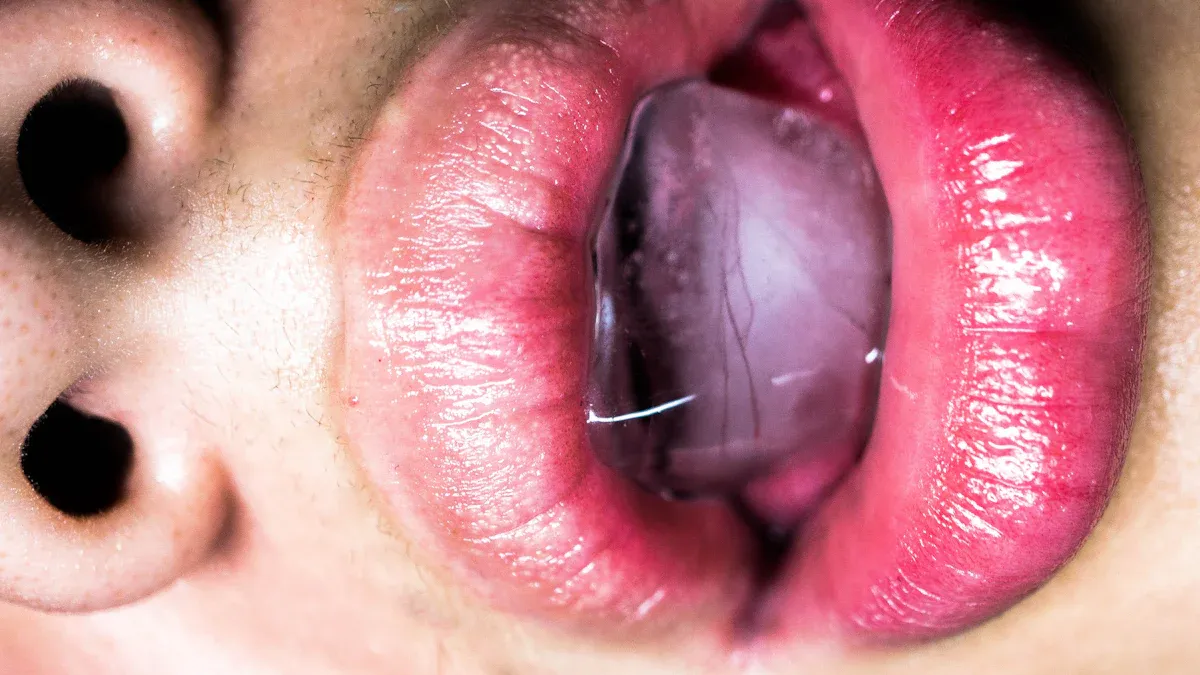
Tonsillitis is an inflammation of the tonsils, often caused by infections. It can affect anyone, but children are more likely to experience it. You should watch for symptoms like a sore throat, fever, and swollen lymph nodes. In some cases, tonsillitis can lead to more serious health issues. Understanding the causes is vital for effective treatment. For instance, studies show that 12.7% of patients in Nigeria had tonsillitis, with the highest prevalence in young children. Being aware of these facts can help you recognize when to seek medical attention.
Key Takeaways
Tonsillitis is an inflammation of the tonsils caused by viral or bacterial infections. Common symptoms include sore throat, fever, and swollen lymph nodes.
Recognizing symptoms early is crucial. If you have a sore throat lasting more than two days or trouble swallowing, contact your healthcare provider.
Viral tonsillitis usually lasts three to four days and often resolves without treatment. Bacterial tonsillitis may require medical attention if symptoms persist.
Stay hydrated and rest to help your body recover from tonsillitis. Over-the-counter pain relievers can also provide relief.
Tonsillitis can be contagious. Practice good hygiene to prevent spreading the infection, especially if caused by viruses or bacteria.
Tonsillitis Symptoms
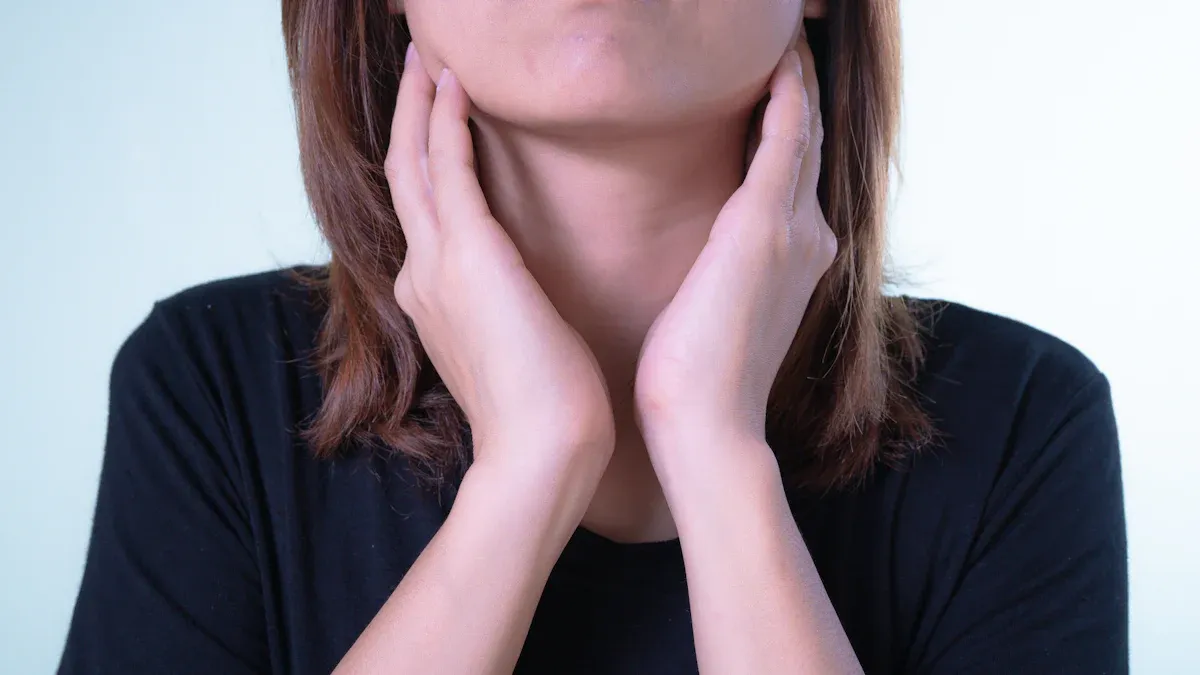

Common Symptoms
When you experience tonsillitis, several common symptoms may arise. These symptoms can help you identify the condition early. Here are the most frequently reported symptoms:
Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
Sore throat | A common complaint in acute tonsillitis. |
Fever | Elevated body temperature, typically between 38°C to 40°C. |
Swollen lymph nodes | Tender swelling over the anterior cervical lymph nodes, indicating lymphadenopathy. |
Dysphagia | Difficulty swallowing, often reported by patients. |
Chills | Accompanying symptoms of fever, indicating systemic infection. |
Research shows that about 67% of individuals with tonsillitis report fever, while 65% experience swollen lymph nodes. These symptoms can significantly impact your daily activities, making it essential to recognize them early.
Less Common Symptoms
In addition to the common symptoms, you may also experience less common symptoms. These can vary from person to person but are still important to note. Some of these symptoms include:
Headache: This can occur due to the infection and inflammation affecting your body.
Earache: Pain in the ear may arise as referred pain. The nerves serving the throat and ears are interconnected, leading to discomfort radiating to the ears. You might notice:
Pain in one or both ears.
A sensation that varies from subtle to sharp or burning.
Additional symptoms like muffled hearing or a feeling of fullness in the ear.
Understanding these symptoms can help you differentiate tonsillitis from other throat infections. For instance, children may exhibit unusual irritability and drooling due to difficulty swallowing, while adults might experience more pronounced headaches and stiff necks.
Recognizing both common and less common symptoms is crucial for timely medical intervention. If you notice these signs, consider consulting a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Tonsillitis Causes
Tonsillitis can arise from two main types of infections: viral and bacterial. Understanding the differences between these causes is crucial for effective treatment and management.
Viral Causes
Viral infections account for a significant portion of tonsillitis cases. Estimates suggest that 40% to 60% of tonsillitis cases result from viral pathogens. Common viruses associated with tonsillitis include:
Rhinovirus
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)
Adenovirus
Coronavirus
Epstein-Barr virus
Cytomegalovirus
Hepatitis A
Rubella
These viruses often lead to milder symptoms compared to bacterial infections. You might notice additional symptoms like cough, congestion, or a runny nose if a virus causes your tonsillitis. Typically, viral tonsillitis symptoms last about three to four days, and they usually resolve without specific medical treatment.
Bacterial Causes
Bacterial infections are another leading cause of tonsillitis. Research indicates that approximately 47% of patients with tonsillitis have bacterial infections. The most common bacterial pathogen responsible for tonsillitis is Group A beta-hemolytic Streptococcus (GABHS), which accounts for 20% to 30% of cases in children and 5% to 15% in adults. Other bacteria, such as Staphylococcus aureus, can also contribute to tonsillitis.
Here’s a summary of the prevalence of different bacterial pathogens:
Bacterial Pathogen | Prevalence in Tonsillitis |
|---|---|
Streptococcus pyogenes | 20-30% in children |
Staphylococcus aureus | Predominant |
Methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) | 39% of isolates |
Bacterial tonsillitis often presents with more severe symptoms, such as intense throat pain and bad breath. Symptoms may last longer than those caused by viral infections, and you should seek medical attention if they persist beyond a few days.
In summary, tonsillitis is an inflammation of the tonsils caused by viral or bacterial infections. You should be aware of common symptoms like sore throat, fever, and swollen lymph nodes. Less common symptoms, such as headaches and earaches, can also occur.
Monitoring your symptoms is crucial. If you experience a sore throat lasting more than two days or have trouble swallowing, contact your healthcare provider. Here’s a quick reference for when to seek help:
Condition | Action to Take |
|---|---|
Sore throat for more than two days | Call your health care provider |
Trouble or pain when swallowing | Call your health care provider |
Feels very sick or very weak | Call your health care provider |
Trouble breathing | Get emergency care right away |
Starts drooling | Get emergency care right away |
Taking these steps can help you manage tonsillitis effectively and ensure a smoother recovery. Remember to follow up with your doctor and take care of yourself during this time.
FAQ
What is tonsillitis?
Tonsillitis is an inflammation of the tonsils, usually caused by viral or bacterial infections. It leads to symptoms like sore throat, fever, and swollen lymph nodes.
How can I treat tonsillitis at home?
You can treat tonsillitis at home by staying hydrated, using throat lozenges, and taking over-the-counter pain relievers. Resting helps your body recover faster.
When should I see a doctor for tonsillitis?
You should see a doctor if your sore throat lasts more than two days, you have difficulty swallowing, or you experience severe symptoms like trouble breathing.
Can tonsillitis be contagious?
Yes, tonsillitis can be contagious, especially if caused by viral or bacterial infections. You can spread it through respiratory droplets when coughing or sneezing.
How long does tonsillitis last?
Viral tonsillitis typically lasts three to four days, while bacterial tonsillitis may persist longer. Seek medical advice if symptoms do not improve within a few days.


