
Omega-3 eggs offer a unique boost to your nutrition. These eggs contain higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids, such as ALA and DHA, which support heart and brain health. You might choose omega-3 eggs if you want to improve your diet and get more nutrients without eating fish.
The global omega-3 eggs market reached USD 100 Billion in 2023 and could grow to USD 147.75 Billion by 2031, showing strong demand for healthier options.
Key Takeaways
Omega-3 eggs provide higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids, supporting heart and brain health.
These eggs are a great option for those who do not eat fish, offering a simple way to boost omega-3 intake.
Pasture-raised omega-3 eggs contain more vitamins and nutrients compared to regular eggs, enhancing your diet.
Incorporating omega-3 eggs into meals can help lower triglycerides and may reduce heart disease risk.
You can easily swap regular eggs for omega-3 eggs in recipes to increase nutritional value.
Omega-3 Eggs Overview

What Are Omega-3 Eggs
You may wonder what makes omega-3 eggs different from regular eggs. Omega-3 eggs contain higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids, which boost their nutritional value. These eggs come from hens that eat special diets. You can find omega-3 enriched eggs, pasture-raised eggs, and organic eggs in stores. Each type offers a unique nutritional profile.
Here is a quick look at how omega-3 content compares:
Egg Type | Omega-3 Content Comparison |
|---|---|
Omega-3 Enriched | 5 times more omega-3 than conventional eggs |
Pastured | 4.5 times more ALA, 2 times more EPA and DHA |
Organic | Little difference compared to conventional eggs |
Pasture-raised eggs and omega-3 enriched eggs have much higher omega-3 levels than regular eggs. Organic eggs do not show much difference in omega-3 content.
How Omega-3 Eggs Are Made
You get omega-3 enriched eggs when farmers feed hens diets rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids. These feeds often include flaxseed, rapeseed, microalgae, canola, or chia. Farmers sometimes add natural antioxidants like grape seed or sea buckthorn meals. These ingredients help improve egg quality and reduce unwanted effects.
Pasture-raised hens eat grass and insects, which also increases omega-3 levels. Organic eggs come from hens fed organic feed, but their omega-3 content stays close to regular eggs.
You can see the nutritional value of omega-3 eggs in this table:
Nutrients | Omega-3 eggs | Conventional eggs |
|---|---|---|
Omega-3 content | High | Normal |
Vitamin E | Higher | Lower |
Saturated fat | Lower | Higher |
Omega-3 enriched eggs offer more nutritional value than regular eggs. You get more vitamin E and less saturated fat. These eggs also have a smaller environmental impact. Farmers use less energy and produce fewer greenhouse gases when making omega-3 eggs.
Omega-3 Eggs Nutrition

Omega-3 Content
You get a significant amount of omega-3 fatty acids when you eat omega-3 eggs. Two omega-3 eggs provide about 180mg of omega-3, which helps you meet your daily nutrition needs. The amount of omega-3 in each egg depends on what the hens eat. Farmers use different diets to boost the omega-3 content in the yolk. You can see how the concentration of DHA changes with different feeds:
Standard diet: 84 mg/100g egg
0.23% OPAO: 195 mg/100g egg
0.76% OPAO: 286 mg/100g egg
0.25% CAO: 183 mg/100g egg
0.69% CAO: 297 mg/100g egg
Most brands in stores offer between 160mg and 225mg of omega-3 per egg. You will not get as much omega-3 as you would from fatty fish like salmon or mackerel, but omega-3 eggs still give you a good boost if you do not eat fish.
Nutrient Comparison
You may wonder how omega-3 eggs compare to regular eggs and fish in terms of nutrition. The yolk in omega-3 eggs contains more omega-3 and other essential nutrients than the yolk in regular eggs. You get high-quality protein from both eggs and fish. You need to eat about three eggs to get the same amount of protein as a 3-ounce serving of salmon. The amount of omega-3 in enriched eggs varies from 100mg to 500mg per egg. By comparison, a 4-ounce serving of salmon gives you six or seven times more omega-3 than a serving of omega-3 eggs.
According to the ODS and USDA Nutrient Database, a conventional egg has 30mg omega-3 fatty acids. The IOM recommends 1.1-1.6g ALA (plant omega-3 fatty acid) daily.
Most common brands found in grocery stores supply 160-225mg omega-3 per egg. While fish like salmon, tuna and mackerel can supply substantially more quality omega-3 fats than omega-3 fortified eggs, this type of egg may be a good option for those that do not eat fish.
You can see the nutrition comparison in this table:
Food | Omega-3 (mg) per serving | Protein (g) per serving |
|---|---|---|
Omega-3 eggs (2) | 180 | 12 |
Regular eggs (2) | 60 | 12 |
Salmon (3 oz) | 1,000+ | 22 |
Other Nutrients
You get more than just omega-3 from omega-3 eggs. Pasture-raised eggs stand out as a nutritional powerhouse. Research shows that eggs from pastured hens contain twice as much vitamin E and 38% more vitamin A than regular eggs. The yolk nutrition in pasture-raised eggs gives you extra essential nutrients that support your health. You also get vitamin D, choline, and selenium from the yolk. These nutrients help your body function well and keep you feeling strong.
In terms of protein, both fish and eggs are high quality protein sources, although you’d have to eat about three eggs to get the same amount of protein as in a 3-ounce serving of salmon. The amount of omega-3 in an enriched egg varies considerably from around 100 to 500 mg per egg. By comparison, a 4-ounce serving of salmon is going to give you six or seven times as much omega-3 as a serving of omega-3 eggs.
You can choose omega-3 eggs to boost your nutrition, especially if you do not eat fish. The yolk in these eggs provides a rich source of vitamins and minerals. Pasture-raised eggs offer even more benefits, making them a smart choice for your diet.
Eggs Benefits
Heart Health
You may want to know what makes omega-3 eggs important for heart health. These eggs give you a source of omega-3, which many people do not get enough of in their diets. When you eat omega-3 eggs, you add healthy fats to your meals. These fats help support your heart and may lower your risk of heart disease. The yolk in each egg contains nutrients that play a role in keeping your heart strong.
Researchers have studied the effects of omega-3 on heart health. Here is what they found:
The Cochrane systematic review shows that increasing long-chain omega-3 fats or ALA likely does not have a large effect on cardiovascular health outcomes.
Moderate evidence suggests that ALA, found in plant oils and nuts, may give a slight protective effect for your heart, but the overall impact is small.
To prevent one person from developing arrhythmia, 143 people would need to increase their ALA intake. To prevent one death from coronary heart disease, 1,000 people would need to do so.
You can see that omega-3 eggs may offer some heart health benefits, but the effect is not dramatic for everyone. If you do not eat fish like salmon, these eggs can help you add more omega-3 to your diet. The yolk in pasture-raised eggs also contains antioxidants and vitamins that support your heart.
Inflammation Reduction
Inflammation can affect your heart and your overall health. You may wonder what benefits eggs offer for inflammation. Scientists have looked at how egg consumption changes inflammation markers in the body. The results are mixed, but some patterns appear.
Inflammatory Biomarker | Weighted Mean Difference (WMD) | 95% Confidence Interval (CI) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
hs-CRP | 0.24 mg/L | −0.43, 0.90 | 0.48 |
IL-6 | 0.20 pg/mL | −0.71, 1.11 | 0.50 |
TNF-α | −0.38 pg/mL | −0.87, 0.10 | 0.12 |
Eating eggs did not significantly change inflammation markers in adults.
In healthy people, eggs may have a small pro-inflammatory effect.
In people who are overweight or obese, eggs might help reduce inflammation.
Eggs contain bioactive components like phospholipids, antioxidants, and proteins. These can have both pro- and anti-inflammatory properties. The cholesterol in eggs does not usually reach levels that cause harm. Some proteins in the yolk, such as ovotransferrin, may help lower inflammation by reducing certain cytokines. This means that the anti-inflammatory benefits of eggs may balance out any possible negative effects.
Blood Lipids
Blood lipids include triglycerides and cholesterol. These are important for heart health. You may ask what benefits omega-3 eggs provide for your blood lipids. Clinical trials show that eating omega-3 enriched eggs can help you lower your blood triglycerides by 15–20%. This is a positive change for your heart.
Omega-3 enriched eggs can cause a small increase in HDL cholesterol, which is the “good” cholesterol.
Total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol, which is the “bad” cholesterol, do not rise much when you eat these eggs.
The yolk in omega-3 eggs gives you healthy fats that support your heart. When you choose pasture-raised eggs, you also get more vitamins and antioxidants. These nutrients work together to give you more health benefits.
Many people with chronic digestive disorders, such as irritable bowel syndrome, can benefit from the gentle protein and nutrients in eggs. The yolk is easy to digest and provides important vitamins for your well-being. You can enjoy the health benefits of eggs as part of a balanced diet.
If you want to improve your heart health, lower inflammation, and support your blood lipids, you can add omega-3 eggs to your meals. These eggs give you a simple way to boost your nutrition and enjoy the benefits of a healthy yolk. Pasture-raised eggs and omega-3 enriched eggs both offer unique health benefits that support your heart and overall well-being.
Why Omega-3 Eggs Matter
Modern Diet Needs
You live in a world where many diets lack enough omega-3. Most people do not eat enough fatty fish or plant-based oils. Omega-3 eggs help fill this gap. They give you a simple way to add more omega-3 to your meals. The table below shows how much omega-3 you need each day:
Age Group | Recommended Daily Intake (g) |
|---|---|
Birth to 6 months | 0.5 |
7–12 months | 0.5 |
1–3 years | 0.7 |
4–8 years | 0.9 |
9–13 years | 1.2 (males), 1.0 (females) |
14–51+ years | 1.6 (males), 1.1 (females) |
Pregnant | 1.4 |
Lactating | 1.3 |
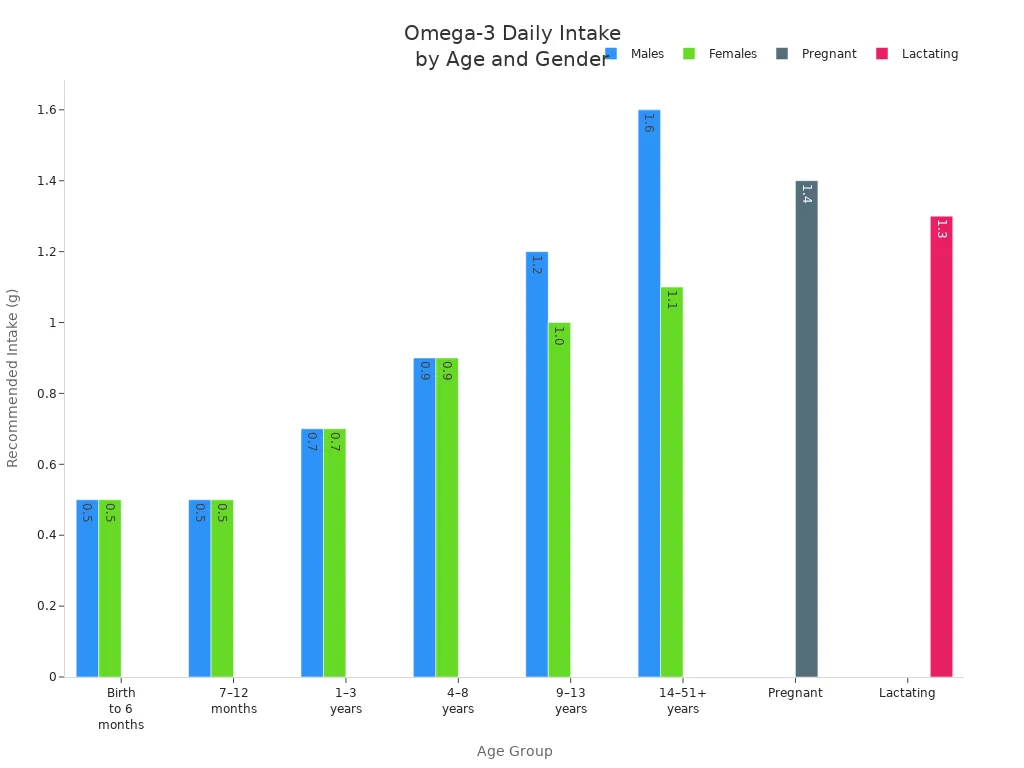
You can get omega-3 from plant-based oils, flaxseed, fatty fish, and omega-3 eggs. Choosing these foods helps you meet your daily needs and supports a sustainable diet.
Who Should Eat Omega-3 Eggs
Some groups benefit more from omega-3 eggs. Active females find these eggs support exercise and recovery. Older adults use omega-3 eggs to help with healthy aging. You may also want to choose pasture-raised eggs if you care about sustainable practices. These eggs come from hens raised with sustainable methods, which protect the environment.
Active females
Older adults
People who do not eat fish
Anyone seeking a sustainable and nutrient-rich diet
Omega-3 eggs give you essential nutrients for health. They help you meet your daily omega-3 needs, especially if you do not eat fish.
Functional Foods
You may wonder what makes omega-3 eggs a functional food. Functional foods give you more than basic nutrition. They help prevent chronic diseases and support your health. Recent research shows that eating more eggs can raise cholesterol, which may increase heart disease risk. However, omega-3 eggs offer benefits like lower triglycerides and anti-inflammatory effects. The table below shows how omega-3 eggs fit into healthy eating patterns:
Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
Classification | The FDA calls eggs a ‘healthy, nutrient-dense’ food. |
Nutritional Benefits | Eggs provide choline, vitamin D, and omega-3 fatty acids. |
Dietary Guidelines | Fits with advice to eat a variety of foods for a healthy diet. |
You can choose pasture-raised eggs for more nutrients and a sustainable choice. These eggs support your health and the planet through sustainable practices.
Using Omega-3 Eggs
Meal Ideas
You can add omega-3 eggs to many meals in your diet. These eggs work well for breakfast, lunch, or dinner. You might choose Eggland’s Best eggs, which contain 125 milligrams of omega-3s, more than double the amount found in ordinary eggs. Adding these eggs to your meals helps you boost your omega-3 intake. Popular options include the Omega-3 Burrito and the Smoked Salmon and Egg Sandwich. You can also try pasture-raised eggs for extra nutrients.
Here are some meal ideas to consider:
Make a breakfast bagel sandwich with turkey bacon and omega-3 eggs.
Prepare tuna patties using omega-3 eggs and sunflower seeds.
Bake banana walnut protein bars with omega-3 eggs for a snack.
Cook cheese and mint pie (Tiropita) with feta, ricotta, and omega-3 eggs.
Try omega meatballs with lean beef and omega-3 eggs.
Tip: You can use omega-3 eggs in most recipes that call for regular eggs. This simple swap increases the nutritional value of your meals.
Cooking Tips
You want to keep the omega-3 content high when you cook eggs. Different cooking methods affect the amount of omega-3 in the final dish. The table below shows how boiling and scrambling change the levels of key omega-3 fatty acids compared to raw eggs:
Cooking Method | C18:3 (LNA) Content | C22:6 (DHA) Content |
|---|---|---|
Raw Eggs | 7.84% | 1.62% |
Boiled Eggs | 7.41% | 1.10% |
Scrambled Eggs | 7.28% | 1.02% |
Boiling and scrambling lower the omega-3 content slightly, but you still get a good amount. You can maximize nutrition by using gentle cooking methods and avoiding high heat for long periods. Many people prefer pasture-raised eggs for their taste and nutrient profile.
You see regional differences in how people use omega-3 eggs. On the West Coast, health-conscious millennials and older adults choose these eggs more often. Some consumers prefer organic options for environmental reasons, while others look for affordable choices. Education about the benefits of omega-3 eggs helps people make better decisions for their diet.
Omega-3 eggs give you a simple way to boost your nutrition. You get more ALA, DHA, and EPA than regular eggs, along with protein and vitamins that support your eyes and heart.
Studies show omega-3 eggs can lower triglycerides and may help reduce heart disease risk.
You can use them in any recipe that calls for eggs, making it easy to add them to your meals.
Try swapping regular eggs for omega-3 eggs at breakfast or in baking to start seeing the benefits.
FAQ
What makes omega-3 eggs different from regular eggs?
Omega-3 eggs contain more omega-3 fatty acids. Farmers feed hens special diets with flaxseed or algae. You get extra nutrients that support your heart and brain.
What is the best way to store omega-3 eggs?
You should keep omega-3 eggs in the refrigerator. Store them in the original carton. This helps protect the eggs from light and keeps them fresh longer.
What recipes work well with omega-3 eggs?
You can use omega-3 eggs in any recipe that calls for regular eggs. Try scrambled eggs, omelets, or baking.
Tip: Use gentle cooking methods to keep more nutrients.
What are the main health benefits of omega-3 eggs?
Omega-3 eggs help support heart health. You get healthy fats, vitamins, and protein. These eggs may lower triglycerides and reduce inflammation.
What should you look for when buying omega-3 eggs?
Check the label for “omega-3 enriched” or “pasture-raised.”
Label Type | Omega-3 Level | Extra Nutrients |
|---|---|---|
Omega-3 Enriched | High | Yes |
Pasture-Raised | Moderate | Yes |
Organic | Low | No |
