Cocoa butter comes from cocoa beans and appears in many foods and skincare products. You find it in chocolate and lotions. Most chocolate uses cocoa butter. Check out the table below to see key facts about Cocoa Butter Nutrition and discover health benefits like heart support, antioxidant power, and easy digestion.
Nutrient | Amount per Serving |
|---|---|
Calories | 120 |
Protein | 0 grams |
Fat | 14 grams |
Carbohydrates | 0 grams |
Fiber | 0 grams |
Sugar | 0 grams |
Vitamins | Vitamin K, Vitamin E, Choline |
Key Takeaways
Cocoa butter is a rich source of healthy fats and antioxidants, making it beneficial for skin hydration and heart health.
Use cocoa butter in moderation due to its high saturated fat content, which can increase heart disease risk if consumed excessively.
Incorporate cocoa butter into recipes for a creamy texture in desserts or as a vegan substitute for animal fats.
What Is Cocoa Butter?

Definition
You find cocoa butter in chocolate and many skincare products. Cocoa butter comes from the fat inside cocoa beans. You see it as a pale yellow, solid fat that melts easily. People use it because it feels smooth and has a mild chocolate scent. Cocoa Butter Nutrition stands out because it contains special fats called triglycerides. These fats help give chocolate its smooth texture and help your skin stay soft.
The main fatty acids in cocoa butter include palmitic acid, oleic acid, and stearic acid. You can see the breakdown in the table below:
Fatty Acid | Percentage |
|---|---|
Oleic acid (C18:1) | 34.5% |
Stearic acid (C18:0) | 34.5% |
Palmitic acid (C16:0) | 26.0% |
Linoleic acid (C18:2) | 3.2% |
Arachidic acid (C20:0) | 1.0% |
Palmitoleic acid (C16:1) | 0.3% |
Other Fatty Acids | 0.5% |
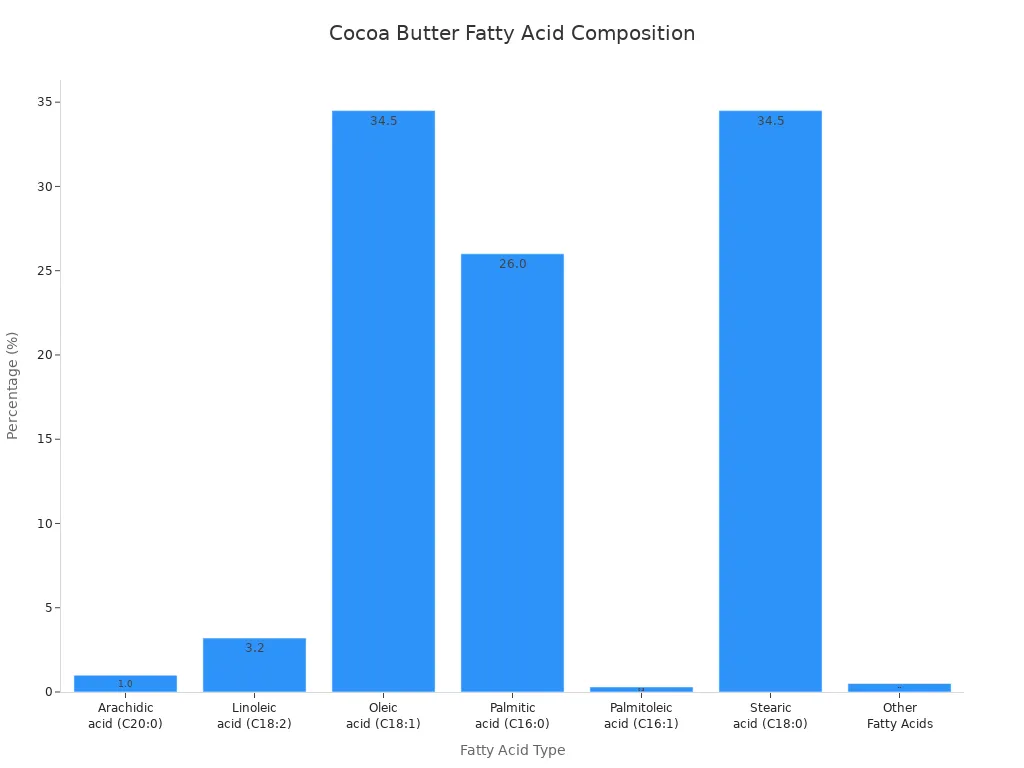
You also find that the main triglycerides in cocoa butter are POP, POS, and SOS. These names come from the types of fatty acids they contain.
How It’s Made
You might wonder how cocoa butter gets from the bean to your chocolate bar or lotion. The process starts with cocoa beans. Workers ferment, dry, roast, and peel the beans. Next, machines grind the beans into a thick liquid called cocoa liquor. Presses squeeze this liquor to separate cocoa butter from cocoa solids.
Here is a simple overview of the steps:
Ferment, dry, roast, and peel cocoa beans.
Grind beans to make cocoa liquor.
Press cocoa liquor to extract cocoa butter.
Use special machines that control pressure and temperature for safety and quality.
Step/Aspect | Description/Details |
|---|---|
Initial Processing | Seeds are fermented, dried, roasted, and peeled before grinding and pressing. |
Cocoa Liquor Formation | Continuous crushing of roasted cocoa beans forms a rich liquid known as cocoa liquor. |
Extraction Method | The cocoa liquor is pressed to separate cocoa butter from cocoa solids. |
Machinery Standards | Equipment must comply with FDA, EU 1935/2004, and GMP standards for food safety. |
Key Technical Specifications | Pressure capacity (15-40 MPa), temperature control precision (±1°C), throughput (50-700kg/h). |
You see that each step helps keep the cocoa butter pure and safe for you to use in food or skincare.
Cocoa Butter Nutrition

Key Nutrients
You get important nutrients from cocoa butter. This fat contains antioxidants that help your body fight inflammation and free radicals. You also find omega-3 fatty acids, which support your brain and vision. Vitamin E in cocoa butter helps your immune system stay strong.
Antioxidants help protect your cells.
Omega-3 fatty acids support your brain and eyes.
Vitamin E boosts your immune health.
Cocoa Butter Nutrition stands out because it does not contain protein or carbohydrates. You see only pure fat in its nutrition profile.
Nutrient | Value | Daily Value % |
|---|---|---|
Protein | 0g | 0% |
Carbs | 0g | 0% |
You can compare cocoa butter to other plant-based fats. The table below shows the fatty acid content in cocoa butter and similar fats:
Fat raw material | C16:0 (%) | C18:0 (%) | C18:1 (%) | C18:2 (%) | Typical triacyl glyceride content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Cocoa butter | 25 | 35 | 35 | 3 | 16 |
Illipe butter | 20 | 42 | 36 | 4 | 7 |
Palm oil | 44 | 4 | 45 | 10 | 26 |
Palm kernel oil | 8 | 2 | 15 | 3 | Trace |
Shea butter | 4 | 41 | 47 | 5 | Trace |
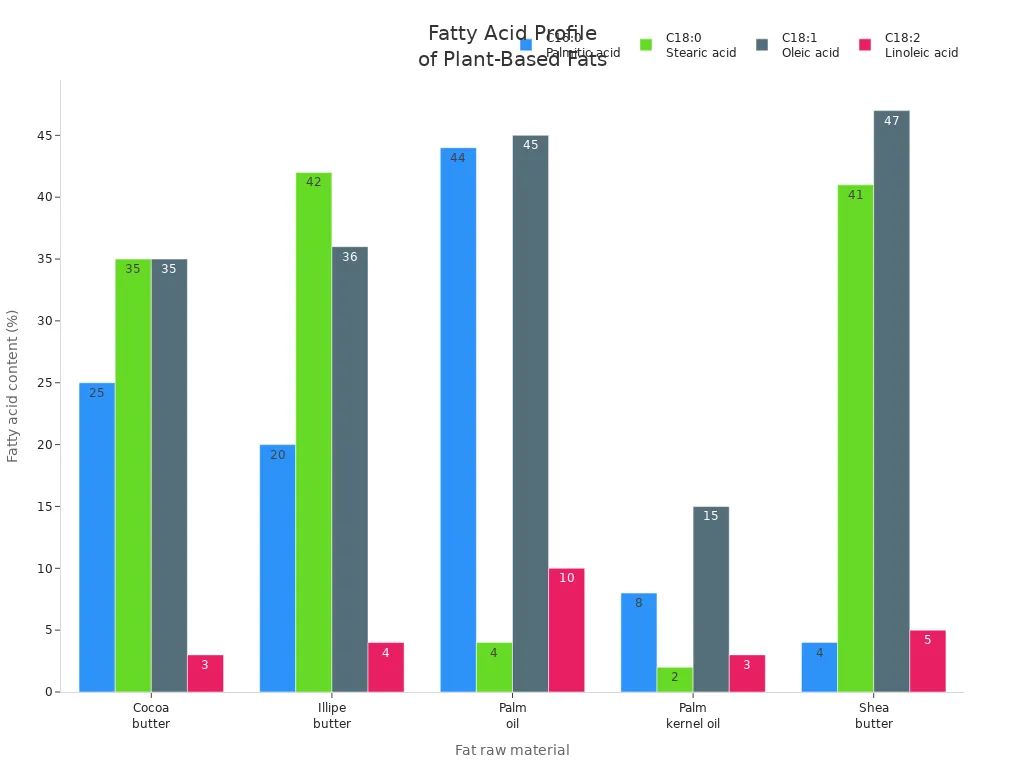
Calorie and Fat Content
You get most of your calories from fat when you eat cocoa butter. One tablespoon gives you about 120 calories. Some sources say you might get 40 calories, but most agree on 120 calories per tablespoon.
120 calories per tablespoon (most sources)
40 calories per tablespoon (some sources)
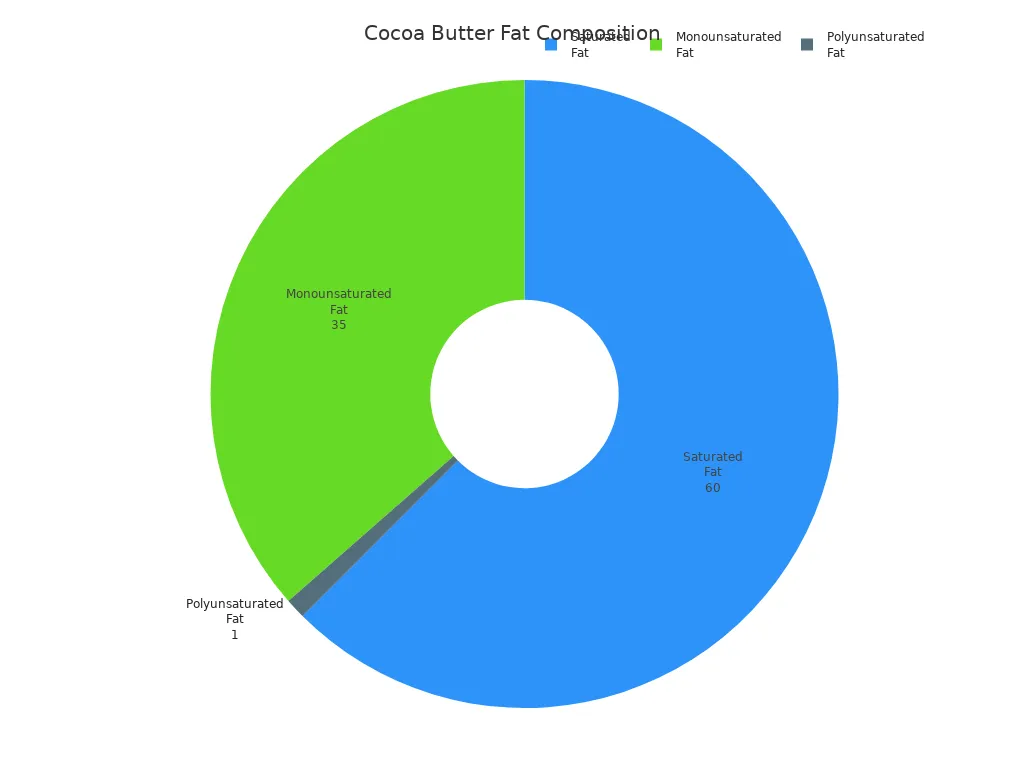
Cocoa Butter Nutrition includes a high amount of fat. You find both saturated and unsaturated fats. Saturated fat makes up about 60% of the total fat. Monounsaturated fat is about 35%, and polyunsaturated fat is about 1%.
Type of Fat | Percentage of Total Fat |
|---|---|
Saturated Fat | ~60% |
Monounsaturated Fat | ~35% |
Polyunsaturated Fat | ~1% |
You also see a breakdown of fatty acids:
Type of Fat | Percentage of Total Fat |
|---|---|
Palmitic Acid | ~25% |
Linoleic Acid | ~3% |
Stearic Acid | ~35% |
Oleic Acid | ~35% |
Other Fatty Acids | ~2% |
You do not get any protein or carbohydrates from cocoa butter. This makes it a pure source of fat.
Tip: If you want to add healthy fats to your diet, cocoa butter gives you a mix of saturated and unsaturated fats.
Glycemic Index
You do not need to worry about blood sugar when you use cocoa butter. Cocoa Butter Nutrition shows that it has a low glycemic index. This means it does not raise your blood sugar. Cocoa butter contains no carbohydrates, so it does not affect your glucose levels.
Low glycemic index
No carbohydrates
No effect on blood sugar
If you watch your blood sugar, cocoa butter is a safe choice. You can use it in recipes without changing your glucose levels.
Health Benefits and Risks
Skin Health
You can use cocoa butter to help your skin stay soft and smooth. Many people choose cocoa butter for dry skin and chapped lips. The high fatty acid content helps your skin hold moisture. You may notice less cracking on elbows and knees when you use cocoa butter regularly. Doctors often recommend cocoa butter during pregnancy to keep skin supple and reduce stretch marks. The fatty acids in cocoa butter lower water loss from your skin, which helps keep it hydrated.
Cocoa butter works well for dry skin and chapped lips.
The vitamin E in cocoa butter may protect your skin cells from aging.
You can use cocoa butter to help your skin feel softer and look healthier.
Note: Some people believe cocoa butter heals scars and stretch marks. Clinical studies show that cocoa butter does not work better than a placebo for stretch marks. Experts like Dr. Anthony and Dr. Vij say there is no solid proof that cocoa butter reduces scars or pregnancy stretch marks.
Study Type | Findings |
|---|---|
Clinical Studies | Cocoa butter does not work better than placebo for stretch marks. |
Randomized Controlled Trials | No significant difference between cocoa butter and placebo in preventing or reducing stretch marks. |
Heart and Metabolic Health
You may wonder if cocoa butter is good for your heart. Cocoa Butter Nutrition includes a high amount of saturated fat. Eating too much saturated fat can raise your risk of heart disease. Studies show that people who eat the most saturated fatty acids, like palmitic acid and stearic acid found in cocoa butter, have an 18% higher risk of heart disease.
High saturated fat intake is linked to heart disease.
Palmitic acid and stearic acid in cocoa butter may increase this risk.
Cocoa butter can also affect your metabolism. Recent studies in mice show that cocoa butter-based high-fat diets can cause gut problems and liver inflammation. These diets may lead to poor glucose tolerance and insulin resistance. Fish oil-based diets did not cause these problems.
Cocoa butter-based diets may cause gut and liver issues.
These diets can lead to insulin resistance and poor glucose tolerance.
Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects
You get antioxidants from cocoa butter that help protect your body. These antioxidants fight free radicals and lower inflammation. Some antioxidants in cocoa butter include epicatechin, isoquercitrin, and quercetin.
Antioxidant | Anti-Inflammatory Effect |
|---|---|
Epicatechin | Reduces secretion of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-8 in blood cells. |
Isoquercitrin | Suppresses production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. |
Quercetin | Acts as an antioxidant and pain reliever, raising pain threshold through several mechanisms. |
You may also get some protection against sun damage and aging. Cocoa butter contains antioxidants that help fight free radical damage, which can cause wrinkles and skin discoloration. Theobromine in cocoa beans may prevent photodamage and reduce wrinkle formation. Cocoa butter’s anti-inflammatory properties help guard against long-term skin damage and aging.
Evidence Type | Description |
|---|---|
Antioxidant Protection | Cacao can fight free radical damage to the skin, which is linked to wrinkles and discoloration. |
UV Protection | Cacao may provide some level of UV protection, helping to prevent skin damage. |
Photodamage Prevention | Theobromine in cocoa beans has shown to prevent photodamage and reduce wrinkle formation in studies. |
Antioxidant Effects | Cocoa’s antioxidants act as free radical scavengers, protecting against UV damage and supporting skin repair. |
Anti-inflammatory Properties | Cocoa butter’s anti-inflammatory properties help guard against long-term skin damage and aging. |
Potential Downsides
You should know about the risks of using cocoa butter. Eating too much cocoa butter can raise your saturated fat intake. This may increase your risk of heart disease. Some people may have skin reactions when they use cocoa butter. You might notice hives, rashes, eczema, or general skin irritation.
High saturated fat intake from cocoa butter is linked to heart disease.
You may experience skin irritation, hives, rashes, eczema, or itching.
Tip: Always test a small amount of cocoa butter on your skin before using it widely. If you notice any irritation, stop using it.
Some claims about cocoa butter are not proven. You may hear that cocoa butter heals scars or prevents stretch marks, but studies do not support these claims.
How to Use Cocoa Butter
In Food
You can use cocoa butter in many recipes. This ingredient adds richness and a smooth texture to chocolate and desserts. Cacao butter is essential for making chocolate bars and truffles. You can also use it in gourmet cooking to make dishes taste better. Many people replace cow’s butter with cocoa butter in both sweet and savory recipes. Vegan cooks often choose cocoa butter as a substitute for animal fats. Cocoa butter helps pastries and baked goods have a glossy finish and a mild chocolate flavor.
Cacao butter enhances chocolate truffles and desserts.
You can use it in baking for a firmer, fudgier texture in brownies.
Cookies made with cocoa butter taste buttery and light, like shortbread.
Tip: If you use only cocoa butter in cookies, they may turn out dry and crumbly. Mix cocoa butter with other fats for the best texture.
In Skincare
You can add cocoa butter to your daily skincare routine. Start your morning with a gentle cleanser, then apply a cocoa butter moisturizer to lock in hydration. Cocoa butter works well for deep hydration and protection. Many people use it after showering, while skin is still damp, for better absorption. At night, you can use thicker balms or overnight masks with cocoa butter for extra nourishment. Cocoa butter is ideal for moisturizing, but shea butter is better for soothing and repairing skin.
Apply cocoa butter after cleansing for soft, hydrated skin.
Use cocoa butter masks or serums at night for deeper care.
Cocoa butter helps with stretch marks and dry patches.
Tips and Recipes
Try adding cocoa butter to smoothies, homemade chocolate, or baked goods. Melt cocoa butter and blend it into energy bars or drizzle it over popcorn for a unique treat. For skincare, mix cocoa butter with coconut oil to make a simple body balm. You can also create a lip balm by combining cocoa butter, beeswax, and a drop of essential oil.
Recipe Idea | How to Use Cocoa Butter |
|---|---|
Chocolate Truffles | Melt and blend with cocoa powder |
Body Balm | Mix with coconut oil |
Lip Balm | Combine with beeswax and oils |
Note: Always test a small amount on your skin before using new cocoa butter products.
Cocoa butter gives you essential fatty acids, antioxidants, and polyphenols that support skin and heart health. You can use it to hydrate your skin or add healthy fats to recipes.
Remember: moderation matters because of its high saturated fat.
Many experts suggest you balance benefits with risks before making cocoa butter part of your routine.
Tip: Choose pure cocoa butter for best results in both food and skincare.
FAQ
Can you eat cocoa butter raw?
You can eat cocoa butter raw. It tastes mild and creamy. Many people use it in smoothies, desserts, or homemade chocolate.
Tip: Choose food-grade cocoa butter for safety.
Does cocoa butter clog pores?
Cocoa butter may clog pores for some people. If you have oily or acne-prone skin, test a small area first.
Skin Type | Risk of Clogging |
|---|---|
Dry | Low |
Oily/Acne-prone | High |
Is cocoa butter vegan?
Yes, cocoa butter is vegan. It comes from cocoa beans. You can use it in plant-based recipes and skincare.
Great for vegan baking
Safe for cruelty-free skincare



