
You discover lentils as a powerhouse of nutrition, packed with protein, fiber, and key minerals. More adults and children now enjoy lentils, with consumption rates rising in recent years:
Adults: 6% in 2017–2018
Children: 3% in 2017–2018
Lentils nutrition benefits support your muscles, digestion, and heart. They offer high protein and fiber, low fat, and essential minerals. You also help the planet by choosing lentils, since they have the lowest greenhouse gas emissions and energy demand among protein sources.
Metric | Lentils (Pulses) |
|---|---|
Cost per 100g | Among the lowest-cost protein sources |
Greenhouse Gas Emissions | Lowest GHGE |
Energy Demand | Lowest energy demand |
Sustainability | Most sustainable foods |
Key Takeaways
Lentils are a nutrient powerhouse, providing high protein, fiber, and essential minerals while being low in fat and sodium.
Regular consumption of lentils supports heart health by lowering cholesterol and improving blood sugar control.
Lentils are versatile and can be easily added to various dishes, enhancing both flavor and nutrition.
Eating lentils helps with digestion due to their high fiber content, promoting gut health and regularity.
Lentils are environmentally friendly, with low greenhouse gas emissions and energy demands compared to other protein sources.
Lentils Nutrition Benefits
Nutritional Overview
You find lentils as one of the most nutrient-rich foods available. Lentils nutrition benefits come from their impressive balance of macronutrients and micronutrients. When you eat 100 grams of cooked lentils, you get a food that is low in fat and sodium, yet high in protein, fiber, and complex carbohydrates. This makes lentils a smart choice for anyone who wants to support their health.
Nutrient | Amount per 100g |
|---|---|
Total Fat | 0.38g |
Sodium | 2mg |
Total Carbohydrate | 20g |
Dietary Fiber | 7.9g |
Protein | 9g |
Lentils nutrition benefits include a high amount of dietary fiber, which helps you feel full and supports regular digestion. You also get a good source of plant-based protein, which helps your muscles stay strong. The low fat and sodium content in lentils means you can enjoy them without worrying about unhealthy fats or excess salt.
Tip: Lentils provide complex carbohydrates that give you steady energy throughout the day.
Lentils nutrition benefits stand out when you compare them to other plant-based protein sources. Lentils, beans, chickpeas, and peas all offer protein, fiber, and important nutrients. Lentils contain no cholesterol and very little fat, making them a healthy choice for your meals.
Key Vitamins and Minerals
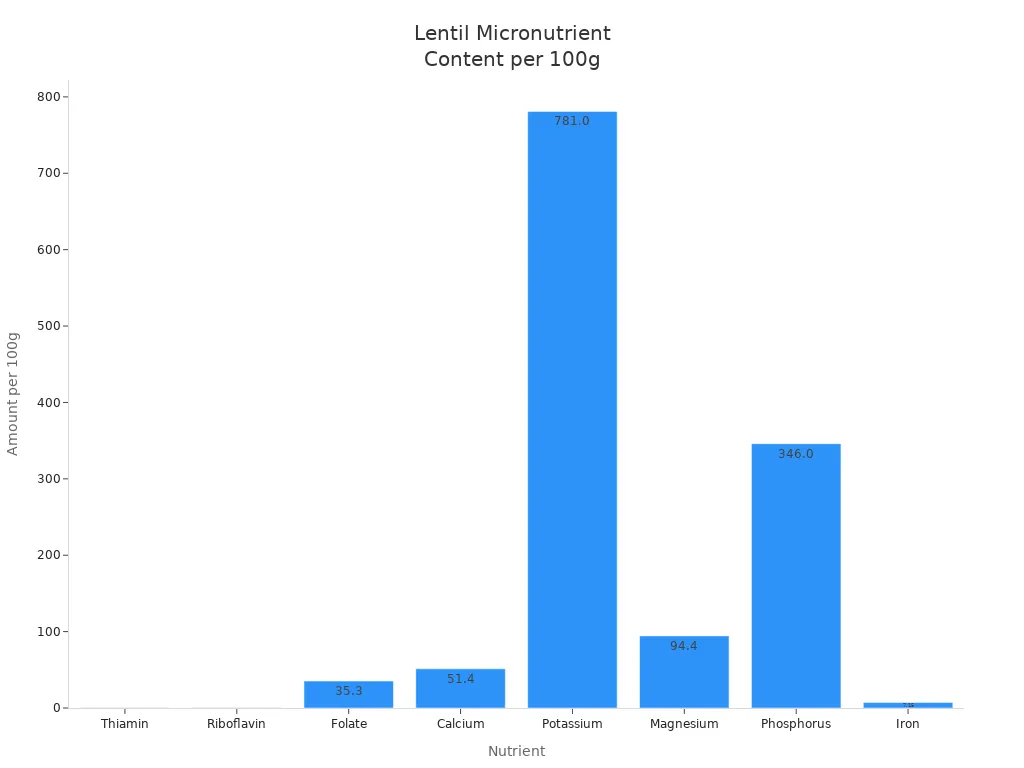
Lentils nutrition benefits go beyond protein and fiber. You get a wide range of vitamins and minerals that help your body work well. Lentils are rich in B vitamins, iron, magnesium, potassium, zinc, and folate. These nutrients play important roles in your energy levels, immune system, and overall health.
Nutrient | Amount per 100g |
|---|---|
Thiamin | 0.28 mg |
Riboflavin | 0.20 mg |
Folate | 35.30 µg |
Calcium | 51.40 mg |
Potassium | 781.00 mg |
Magnesium | 94.40 mg |
Phosphorus | 346.00 mg |
Iron | 7.15 mg |
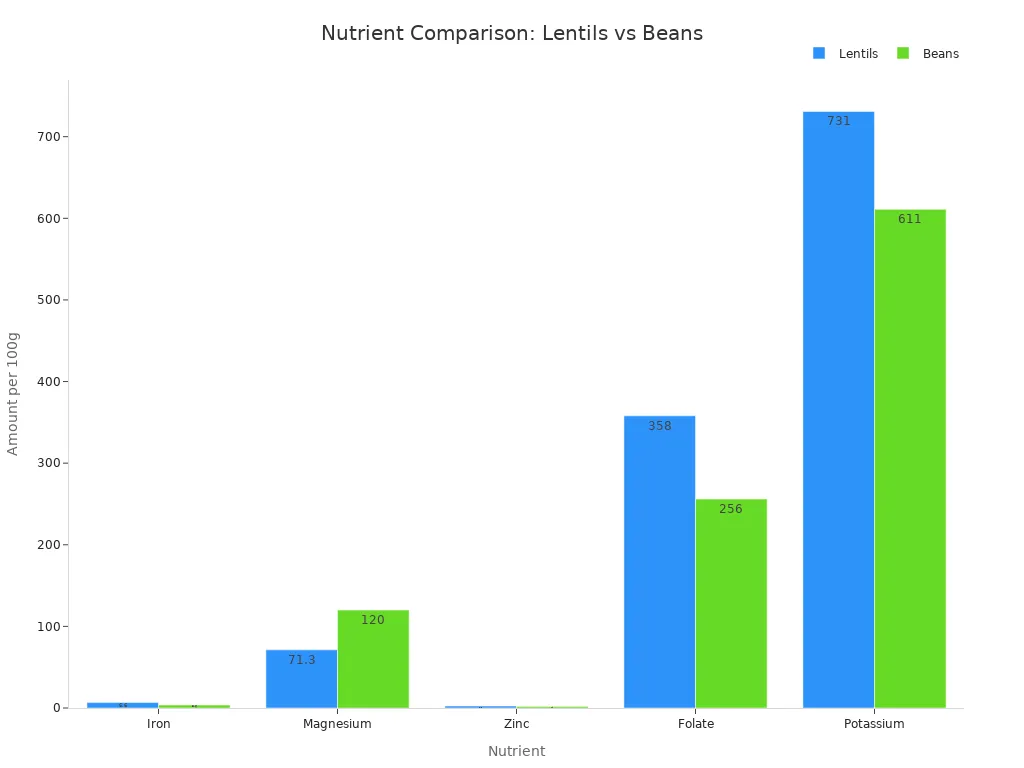
You get more potassium, phosphorus, manganese, and iron from lentils than from canned beans. Lentils also have higher levels of folate and zinc. Folate helps your body make new cells, while iron supports healthy blood. Magnesium and potassium help your muscles and nerves work well.
Nutrient | Lentils | Beans |
|---|---|---|
Iron | 6.6 g | 3.6 g |
Magnesium | 71.3 mg | 120 mg |
Zinc | 2.5 mg | 1.9 mg |
Folate | 358 mcg | 256 mcg |
Potassium | 731 mg | 611 mg |
You also benefit from antioxidants in lentils. These nutrients help protect your cells from damage and may lower your risk of chronic diseases. Lentils nutrition benefits include helping your heart, supporting your immune system, and keeping your bones strong.
Different varieties of lentils offer similar nutrition benefits, but each has its own highlights:
Lentil Variety | Nutritional Highlights | Cooking Time | Flavor Profile |
|---|---|---|---|
Brown Lentils | High in protein, fiber, folate, iron, manganese | 20-30 minutes | Earthy flavor, holds shape well |
Green Lentils | High in protein, fiber, antioxidants | 30-40 minutes | Peppery flavor, retains shape |
Red Lentils | High in protein, fiber, folate, iron | 15-20 minutes | Sweet, nutty flavor, tends to break down |
You can choose brown lentils for soups and stews, green lentils for salads, and red lentils for curries. No matter which type you pick, you get the same core lentils nutrition benefits.
Note: Lentils are gluten-free and cholesterol-free, so you can enjoy them even if you have dietary restrictions.
Lentils nutrition benefits make them a top choice for anyone who wants to add more nutrients to their diet. You get protein, fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants in every serving.
Protein and Fiber in Lentils

Protein Content
You get a high protein content when you eat lentils. One cup of cooked lentils provides about 18 grams of protein. This amount helps you meet your daily recommended intake, which is 56 grams for men and 46 grams for women. Lentils offer plant-based protein that supports your body’s needs. You find lentils as a quality protein source, especially when you combine them with grains. This combination gives you a more complete amino acid profile.
Protein Source | Digestibility Improvement | Comparison to BSA |
|---|---|---|
Lentil Protein Isolates (LPI) | 35–53% | Similar long-term digestibility |
Lentils contain essential amino acids. These nutrients help your muscles grow, repair, and stay strong. You also get micronutrients like iron, magnesium, and zinc, which support muscle function and energy metabolism. Studies show that diets with lentils help maintain muscle mass, especially for active people and older adults.
Fiber Content
Lentils are high in fibre. You get about 15.6 grams of dietary fiber in one cup of cooked lentils. This makes lentils an excellent source of fibre for your diet. Lentils contain both soluble and insoluble fibre. Soluble fibre helps lower cholesterol and control blood sugar. Insoluble fibre adds bulk to your stool and supports regular bowel movements.
Dietary fiber content in lentils: 15.6 grams per cup (198 grams) of cooked lentils.
Lentils increased fecal weight significantly, showing improved bowel function.
Fecal nitrogen levels were higher with lentil consumption, supporting digestive health.
Lentils provide more fiber than chickpeas and most whole grains. One cup of lentils has about 15.5 grams of fiber, while chickpeas have 12.5 grams. Legumes like lentils give you more fiber than most grains, making them a better choice if you want to increase your fiber intake.
Benefits of Lentils for Muscle and Digestion
You benefit from the high protein content and fibre in lentils. Lentils help your muscles grow and repair. They also support muscle maintenance, which is important for active people and older adults. Lentils are recognized as a plant-based protein source essential for muscle health. You get essential amino acids and micronutrients that help your muscles work well.
Lentils are rich in essential amino acids, which help build and repair muscle.
Lentils provide iron, magnesium, and zinc, supporting muscle function and energy.
Adequate protein intake from lentils helps maintain muscle mass.
You also experience the benefits of lentils for digestion. Lentils are high in fibre, which helps regulate your appetite and keeps you feeling full longer. The fibre in lentils promotes the growth of beneficial gut bacteria. This supports gut health and helps control your appetite.
Evidence Description | Findings | Implications |
|---|---|---|
Long-term lentil consumption | Reduced postprandial IL-1β and IL-17 responses | Suggests improved gut health and reduced inflammation |
Increased fiber intake from lentils | Promotes growth of beneficial gut bacteria | Enhances gut health and appetite regulation |
SCFAs production from lentil fermentation | Reduces colonic inflammation and improves gut barrier integrity | Supports digestive health and appetite control |
Lentils do not increase gastrointestinal symptoms, even with high intake. You can eat lentils regularly and enjoy their health benefits. Lentils help improve fasting blood lipid profiles and may aid in appetite control and metabolic health.
Nutrient | Amount per Cup of Cooked Lentils | Daily Recommended Intake |
|---|---|---|
Protein | 18 grams | 56 grams (men), 46 grams (women) |
Fiber | 16 grams | 25 grams (women), 38 grams (men) |
Lentils support weight management. The high protein content and fibre help you feel full and satisfied. Lentils may reduce appetite and help manage obesity. Studies show an inverse association between lentil consumption and obesity or diabetes.
Lentils increased fecal weight, indicating improved bowel function.
Lentils contain prebiotic carbohydrates that promote a healthy gut ecosystem.
Insoluble fiber in lentils adds bulk to stool, aiding regularity.
Tip: A diet rich in fibre from lentils may decrease the risk of various cancers and help prevent heart disease and high blood pressure.
You find the benefits of lentils in every serving. Lentils are high in fibre and protein, making them a smart choice for muscle health, appetite control, and digestive wellness.
Benefits of Lentils for Heart and Health
Heart Health
You support your heart health when you add lentils to your meals. Lentils contain fiber, low fat, and antioxidants, which help lower cholesterol and protect your heart. A review of 26 randomized controlled trials found that eating one serving of lentils or other legumes daily can reduce LDL cholesterol by 5%. You also see improvements in metabolic markers, such as lower fasting LDL cholesterol and better glucose levels. Fiber in lentils binds bile acids, which helps decrease cholesterol in your blood. Saponins in lentils help regulate lipid metabolism.
Findings | Details |
|---|---|
Reduction in LDL cholesterol | Daily lentil consumption for 12 weeks decreased fasting LDL cholesterol |
Improvement in metabolic markers | Long-term lentil consumption improved glucose and inflammation |
Mechanism | Fiber and saponins help lower cholesterol and regulate lipids |
Lentils offer several health benefits for your heart. You get fiber that reduces LDL cholesterol, low fat that replaces meat and lowers risk of heart disease, and antioxidants that support overall heart health. Potassium, calcium, and magnesium in lentils help regulate blood pressure.
Property | Contribution to Cardiovascular Health |
|---|---|
Fiber | Reduces LDL cholesterol, linked to lower incidence of cardiovascular disease |
Low Fat | Replacing meat with lentils decreases the risk of heart disease |
Antioxidants | Essential vitamins and minerals support heart health |
Potassium | Helps decrease blood pressure naturally |
Calcium | Supports blood pressure regulation |
Magnesium | Maintains normal blood pressure levels |
Tip: You can improve your heart health by choosing lentils instead of high-fat meats.
Blood Sugar Control
You help maintain normal blood sugar level when you eat lentils. Lentils have a low glycemic index and a complex macronutrient profile. The protein and fiber in lentils slow down the absorption of sugar into your bloodstream. Studies show that lentils lower blood glucose levels in people with and without diabetes. You can improve glycemic control by including lentils in your meals. Regular lentil consumption supports better blood sugar management.
Chronic Disease Prevention
You lower your risk of heart disease and other chronic conditions by eating lentils. Lentils provide health benefits that include reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes and certain cancers. Research shows that people who eat the most lentils have a hazard ratio of 0.67 for chronic diseases compared to those who eat the least. Higher adherence to plant-based diets, including lentils, links to a reduced risk of type 2 diabetes. Updated clinical practice recommendations highlight the importance of legumes in lowering the risk of major chronic diseases.
Consumption Level | Hazard Ratio (HR) | 95% Confidence Interval (CI) | P-trend |
|---|---|---|---|
Most Lentils | 0.67 | 0.46, 0.98 | 0.05 |
Higher adherence to plant-based diets is linked to a reduced risk of type 2 diabetes.
Emphasizing healthy plant-based foods, including lentils, strengthens the association with reduced diabetes risk.
Antioxidant Effects
You gain health benefits from the antioxidants in lentils. Lentils contain phenolic compounds, tannins, flavonols, and anthocyanins, which help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation. These antioxidants increase the levels of enzymes like superoxide dismutase and catalase, protecting your cells from damage. Lentils also lower malondialdehyde levels, a marker of oxidative stress. Saponins in lentils reduce pro-inflammatory cytokines and improve lipid profiles. You protect your body from oxidative damage and support your immune system by eating lentils.
Note: Lentils provide a rich source of antioxidants that help fight inflammation and keep your body healthy.
Practical Tips and Considerations

Cooking and Meal Ideas
You can enjoy lentils in many ways. They fit into a wide range of dishes, making them one of the most versatile healthy food options. Here are some popular and nutritious ways to prepare them:
Cook lentils well to improve digestibility.
Soak or sprout lentils before cooking to help your body absorb more nutrients and reduce digestive discomfort.
Add spices like cumin, black pepper, turmeric, or ginger for extra flavor and health benefits.
Use lentils in veggie burgers, hearty soups, or fresh salads.
Cooking methods can affect the nutrients in lentils. Traditional boiling may cause some loss of heat-sensitive nutrients. Pressure cooking and vacuum cooking help keep more nutrients and preserve texture. Boiling in water can help retain protein and minerals but may lower iron and magnesium levels. You can choose the method that best fits your needs and taste.
Tip: Try adding cooked lentils to your favorite pasta sauce or grain bowl for a protein and fiber boost.
Potential Risks
Lentils offer many benefits, but you should know about some potential risks. They contain antinutrients, which can affect how your body absorbs nutrients.
Saponins may interfere with normal nutrient absorption.
Tannins can decrease iron absorption and lower protein digestibility.
Trypsin inhibitors may limit protein use by blocking digestive enzymes.
Phytic acid can reduce the absorption of important minerals.
Eating too many lentils may cause gas or bloating because of their high fiber content. People with kidney problems should watch their potassium intake, as lentils are high in potassium. Raw lentils contain lectins, which can cause digestive issues, so always cook them well. Some people may have allergies to lentils, especially if they react to other legumes.
Risk/Side Effect | Description |
|---|---|
Antinutrients | Compounds like trypsin inhibitors and phytic acid hinder nutrient absorption |
Gas and Bloating | High fiber can cause digestive discomfort |
Hyperkalemia | Excess potassium may harm those with kidney issues |
Lectins | Raw lentils may cause digestive problems |
Allergic Reactions | Some people may be allergic to lentils |
Note: Soaking, sprouting, and cooking lentils can help reduce antinutrients and make them safer to eat.
You discover lentils as an excellent source of folate and a key part of a nutrient-rich diet. Lentils provide nutritional information that shows they help prevent anemia and boost your iron intake. You support gut health and manage type 2 diabetes by adding lentils to your diabetic diet. Lentils offer high fiber, protein, and antioxidants, making them easy to prepare and versatile for any meal. You choose lentils to prevent anemia and improve heart health.
FAQ
What nutrients do you get from lentils?
You get protein, fiber, iron, magnesium, potassium, and folate from lentils. Lentils also give you antioxidants. These nutrients help your muscles, heart, and immune system stay healthy.
What makes lentils a good protein source?
Lentils give you plant-based protein. You get about 18 grams of protein in one cup of cooked lentils. This helps you build and repair muscles without adding much fat or cholesterol.
What types of lentils can you eat?
You can eat brown, green, red, and black lentils. Each type has a unique flavor and texture. You can use them in soups, salads, curries, or side dishes.
What are the health benefits of eating lentils?
You support your heart, digestion, and blood sugar by eating lentils. Lentils help lower cholesterol, improve gut health, and keep your energy steady.
What should you know before cooking lentils?
You should rinse lentils before cooking. Cooking them well makes them easier to digest. Soaking or sprouting lentils can help reduce antinutrients and improve nutrient absorption.
