A swollen uvula, also known as uvulitis, occurs when the uvula becomes inflamed or enlarged. This condition can lead to discomfort and difficulty swallowing. Understanding the causes of a swollen uvula is crucial for effective management. Common causes include infections, allergies, and trauma. In some regions, the prevalence of uvulitis can reach 15-20%, especially during times of increased upper respiratory infections. Recognizing these causes helps you take appropriate action if symptoms arise.
Key Takeaways
A swollen uvula can result from infections, allergies, trauma, dehydration, or irritants. Recognizing these causes helps you manage symptoms effectively.
Viral and bacterial infections are common causes of uvulitis. Seek medical advice if you experience a sore throat, fever, or difficulty swallowing.
Food and environmental allergies can trigger uvulitis. Identify your allergens to avoid triggers and reduce swelling.
Dehydration can lead to a swollen uvula. Drink plenty of water daily to keep your throat moist and prevent irritation.
If you notice persistent symptoms or difficulty breathing, consult a healthcare professional immediately for proper evaluation.
Swollen Uvula Causes: Infections
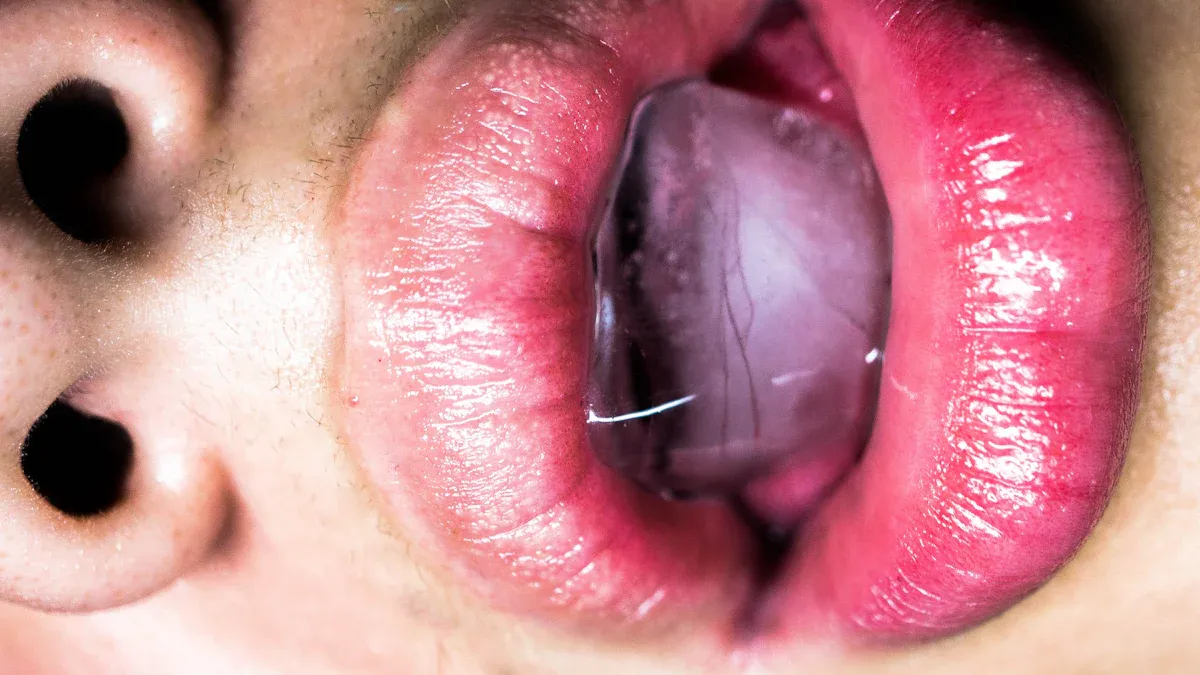
Infections are among the most common causes of a swollen uvula. They can arise from various pathogens, including viruses and bacteria. Understanding these infections can help you identify symptoms and seek appropriate treatment.
Viral Infections
Viral infections often lead to uvulitis. Common culprits include the flu and other upper respiratory viruses. When you contract a viral infection, your body responds with inflammation. This inflammation can cause your uvula to swell.
Strep throat is another viral infection that frequently causes a swollen uvula. You may experience a sore throat, fever, and difficulty swallowing if you have strep throat.
Bacterial Infections
Bacterial infections can also result in a swollen uvula. Several bacterial pathogens are responsible for this condition, including:
Group A streptococcus
Group C and G streptococci
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Fusobacterium necrophorum
Arcanobacterium haemolyticum
These bacteria can infect your throat and lead to inflammation of the uvula. Symptoms may include severe throat pain, fever, and swollen lymph nodes. If you suspect a bacterial infection, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment.
Other Infections
In addition to viral and bacterial infections, fungal infections can cause uvulitis. For instance, Candida albicans has been documented to lead to a swollen uvula. This type of infection often occurs in individuals with weakened immune systems or those who use inhaled corticosteroids.
Recognizing the signs of these infections can help you take action early. If you notice a swollen uvula along with other symptoms, consider seeking medical advice to determine the underlying cause.
Swollen Uvula Causes: Allergies

Allergies can significantly contribute to a swollen uvula. When your body encounters allergens, it may react by inflaming the uvula. Understanding the types of allergies that can lead to this condition is essential for effective management.
Food Allergies
Certain food allergies can trigger uvulitis. When you consume foods that your body identifies as harmful, your immune system responds aggressively. This response can lead to a swollen uvula. Common food allergens include:
Peanuts
Tree nuts
Shellfish
Milk
Eggs
Wheat
Soy
These allergens can cause inflammation in your throat and uvula. The swelling may occur quickly after eating the offending food.
To understand how food allergies trigger uvulitis, consider the following mechanisms:
Mechanism | Description |
|---|---|
Histamine Release | Allergens trigger the immune system to release histamine, leading to inflammation and swelling of tissues, including the uvula. |
Increased Blood Flow | Allergic reactions increase blood flow to affected areas, causing redness, warmth, and swelling of the uvula. |
Fluid Retention | Allergic reactions may cause fluid retention in soft tissues, leading to a swollen uvula. |
Cross-reaction | Proteins in allergens can cross-react with body tissues, resulting in swelling of the uvula. |
Recognizing your food allergies can help you avoid triggers and manage symptoms effectively.
Environmental Allergies
Environmental allergens also play a role in causing a swollen uvula. Common triggers include:
Pollen: Seasonal exposure can inflame the tissues, including the uvula.
Dust Mites: These tiny creatures found in household dust can trigger respiratory and throat reactions.
Pet Dander: Proteins in pets’ skin flakes, saliva, and urine can cause swelling.
Certain Foods: Nuts, shellfish, and dairy are known triggers.
Insect Stings: These can cause localized and systemic allergic responses.
When you encounter these allergens, your body may react similarly to food allergies. The inflammation can lead to discomfort and difficulty swallowing. If you suspect that allergies are causing your swollen uvula, consider consulting a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and management.
Swollen Uvula Causes: Trauma
Trauma can lead to a swollen uvula in various ways. Physical injuries and irritations from medical procedures are common causes. Understanding these factors can help you recognize when to seek medical attention.
Physical Injury
Physical injuries can cause significant swelling of the uvula. Common types of injuries that lead to uvulitis include:
Trauma
Angioedema
Inhalant irritation
Allergy
For example, if you accidentally bite your uvula while eating, it can become inflamed. Additionally, exposure to irritants like smoke or strong chemicals can also lead to swelling.
Irritation from Medical Procedures
Medical procedures can sometimes result in a swollen uvula. While uvulitis is an uncommon complication, it can occur after procedures like intubation or endoscopy. The swelling may arise from compression of the uvula by medical equipment. Risk factors include specific intubation techniques and your pre-existing conditions.
A documented case illustrates this point. A 53-year-old man developed traumatic uvulitis after a suction catheter was accidentally applied to his uvula during a dental appointment. This incident caused severe throat pain and difficulty breathing, highlighting how medical procedures can lead to uvulitis.
If you experience a swollen uvula after a medical procedure, consult your healthcare provider. They can assess your condition and recommend appropriate treatment.
Other Causes of Swollen Uvula
Dehydration
Dehydration can lead to a swollen uvula, a condition known as uvulitis. When you do not drink enough fluids, your body becomes dehydrated. This can cause the mucous membranes around your uvula to dry out. Dry weather can also contribute to this issue. The irritation from dryness can cause inflammation and swelling of the uvula.
To prevent dehydration, make sure you drink plenty of water throughout the day. Aim for at least eight 8-ounce glasses of water daily. If you live in a dry climate or spend time in heated or air-conditioned environments, increase your fluid intake.
Exposure to Irritants
Exposure to various irritants can also cause a swollen uvula. Common irritants include:
Smoking: This habit dries and inflames throat tissues, including the uvula.
Dry Air: Environments with low humidity can dehydrate mucous membranes, making the uvula more prone to soreness.
Chemical Substances: Inhaling substances like tobacco and cannabis can lead to inflammation and swelling of the uvula.
Pollutants: Airborne pollutants, such as sulfur dioxide and particulate matter, can irritate the uvula and contribute to swelling.
Cases of uvulitis have been reported after inhaling substances like cannabis and crack cocaine. Some individuals may experience isolated uvulitis after smoking fentanyl. These reactions can occur due to hypersensitivity, leading to an enlarged and red uvula.
If you notice a swollen uvula and suspect irritants may be the cause, consider reducing your exposure. Avoid smoking and limit time spent in polluted environments.
In summary, a swollen uvula can arise from various causes, including infections, allergies, trauma, dehydration, and exposure to irritants. Recognizing the symptoms of a swollen uvula is crucial for your health. If you notice persistent symptoms or if they interfere with daily activities, consult a doctor. You should seek immediate medical attention if you experience difficulty breathing, fever, or swollen lymph nodes. Staying informed about your health empowers you to take action when necessary.
FAQ
What are the symptoms of a swollen uvula?
You may experience a sore throat, difficulty swallowing, and a sensation of something stuck in your throat. Other symptoms include redness, swelling, and sometimes fever.
How can I treat a swollen uvula at home?
You can try drinking warm fluids, using throat lozenges, and gargling with salt water. Staying hydrated helps reduce swelling. However, consult a doctor if symptoms persist.
When should I see a doctor for uvulitis?
Seek medical attention if you experience severe pain, difficulty breathing, or persistent swelling. These symptoms may indicate a more serious condition requiring immediate care.
Can allergies cause a swollen uvula?
Yes, allergies to food or environmental factors can trigger uvulitis. If you suspect allergies, identify and avoid the triggers to manage your symptoms effectively.
Is uvulitis contagious?
No, uvulitis itself is not contagious. However, the infections that cause it, like strep throat or the flu, can spread from person to person. Practice good hygiene to prevent infections.


