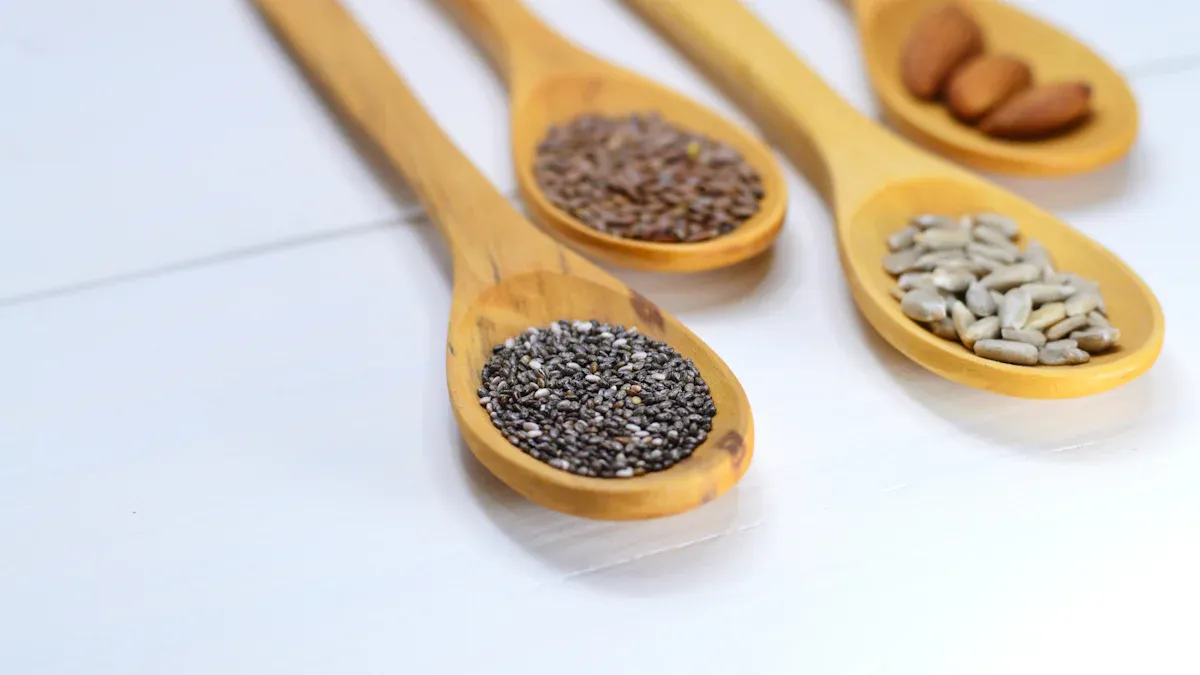
You can find many types of seeds that offer great nutrition and flavor. Seeds like chia, hemp, pumpkin, and sunflower give your body protein, fiber, and healthy fats. Check out the table below to see how much energy, protein, and fiber you get from different seeds and nuts:
Seeds | Energy (kJ) | Protein (g) | Carbohydrate (g) | Fiber (g) | Total fat (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Whole grain flour | 465-1587 | 2.6-15.9 | 23.0-76.9 | 1.8-23.8 | 0.9-6.5 |
Tree nuts and peanuts | 2200-3000 | 7.8-23.7 | 12.3-32.7 | 3.0-12.2 | 46.0-76.1 |
You can sprinkle seeds onto yogurt, salads, or oatmeal for a quick nutrient boost. Explore different Types of Seeds to support your health and add variety to your meals.
Key Takeaways
Seeds are nutritional powerhouses, providing protein, fiber, and healthy fats. Incorporate seeds like chia, flax, and pumpkin into your meals for a health boost.
Different types of seeds offer unique benefits. Oilseeds provide healthy fats, grain seeds offer carbohydrates, and nut-like seeds are rich in fiber. Choose seeds based on your dietary needs.
Adding seeds to your meals is easy. Sprinkle them on yogurt, salads, or oatmeal to enhance flavor and nutrition. Experiment with different seeds to find your favorites.
Soaking or sprouting seeds can improve digestion and nutrient absorption. Try soaking chia or flaxseeds before eating to maximize their health benefits.
Eating a variety of seeds supports overall health. Aim for 1-2 tablespoons daily to enjoy their benefits, including improved heart health and better digestion.
Types of Seeds

You can find many types of seeds in your kitchen and grocery store. These seeds belong to different groups based on their botanical features and nutritional value. Understanding the main types of seeds helps you choose the best ones for your meals.
Seeds fall into three main categories: oilseeds, grain seeds, and nut-like seeds. Each group offers unique nutrients and flavors.
Oilseeds
Oilseeds give you healthy fats and important minerals. You often see these seeds in cooking oils and snacks. Some of the most popular oilseeds include sunflower, soybean, olive, and rapeseed. These seeds contain polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fats, vitamin E, and minerals like phosphorus and calcium.
Oilseed | Nutritional Components |
|---|---|
Sunflower | Polyunsaturated fatty acids, vitamin E, fiber, phosphorus, calcium |
Soybean | Omega-3, omega-6, amino acids, vitamins |
Olive | Monounsaturated fats, antioxidants, vitamin E |
Rapeseed | Omega-3 fatty acids, low saturated fats, vitamin E |
You can add oilseeds to salads, baked goods, or eat them as snacks. These types of seeds help you get more healthy fats and minerals in your diet.
Grain Seeds
Grain seeds come from cereal plants. You eat them every day in foods like bread, rice, and pasta. Wheat, corn, and barley are common grain seeds. These types of seeds provide carbohydrates, fiber, and some protein. Grain seeds differ from other types of seeds because they become easier to digest when sprouted. For example, sprouted barley gives you more antioxidants and enzymes than regular barley.
Tip: Try sprouting grain seeds at home to unlock more nutrients and improve digestibility.
Nut-like Seeds
Nut-like seeds look and taste similar to nuts, but they have different nutrients. Pumpkin seeds and sunflower seeds are good examples. These types of seeds usually have more fiber and omega-3 fatty acids than true nuts. Nuts like almonds and walnuts contain more protein and monounsaturated fats. Nut-like seeds also offer magnesium and zinc, which support your health.
Nutrient Type | Seeds | Nuts |
|---|---|---|
Fiber | Higher | Lower |
Omega-3 Fatty Acids | High in chia, flax | Lower |
Protein | Lower | Higher in almonds, walnuts |
Healthy Fats | Lower calories, fats | Higher monounsaturated fats |
Magnesium | More in pumpkin seeds | Present in cashews |
Zinc | More in pumpkin seeds | Present in Brazil nuts |
Caloric Density | Lower | Higher |
You can use nut-like seeds in trail mixes, smoothies, or sprinkle them on yogurt. Exploring different types of seeds lets you enjoy new flavors and boost your nutrition.
Seed Nutrition
Seeds give you a wide range of nutrition that supports your body every day. You find protein, fiber, healthy fats, vitamins, and minerals in many edible seeds. These tiny foods pack a big punch and help you reach your nutrition goals. When you add seeds to your meals, you boost your energy and help your body stay strong.
Key Nutrients
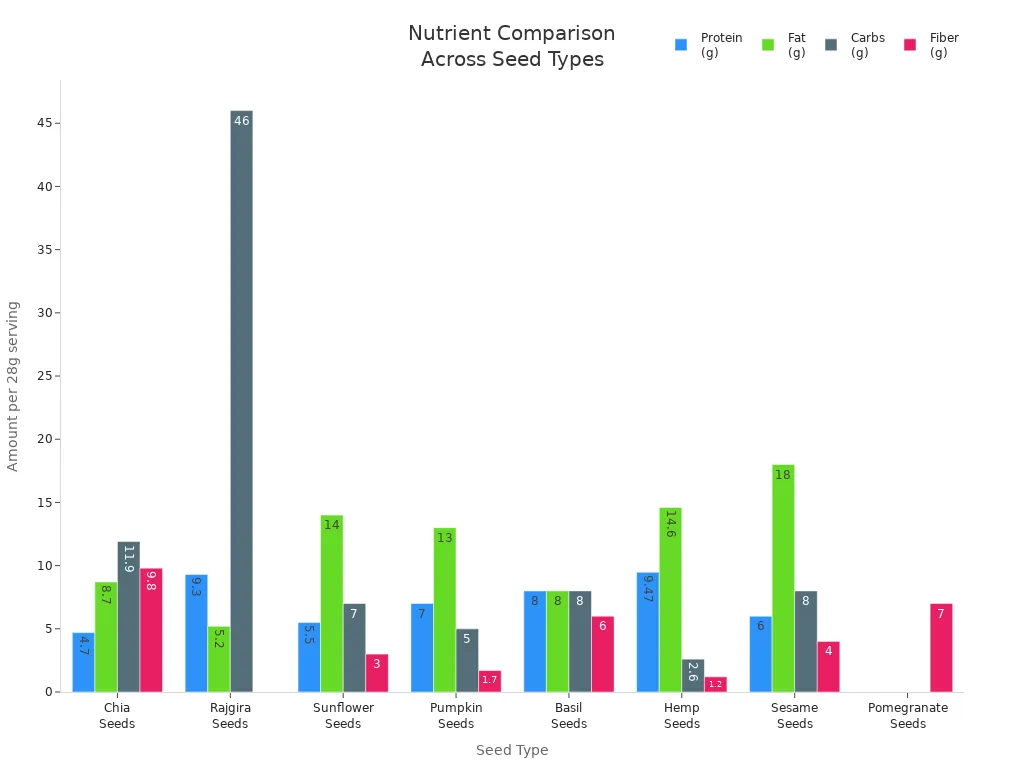
Seeds are nutrient powerhouses. You get plant-based protein, fiber, and healthy fats from seeds like chia, flax, hemp, pumpkin, sunflower, and sesame. Each seed offers a different mix of nutrition. Look at the table below to see how the nutrition levels compare across popular seeds:
Seed Type | Calories | Protein (g) | Fat (g) | Carbs (g) | Fiber (g) | Key Nutrients (RDI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Chia Seeds | 138 | 4.7 | 8.7 | 11.9 | 9.8 | Calcium: 14%, Iron: 12%, Magnesium: 23% |
Sunflower Seeds | 165 | 5.5 | 14 | 7 | 3 | Iron: 6% |
Pumpkin Seeds | 166 | 7 | 13 | 5 | 1.7 | Magnesium: 37%, Iron: 23% |
Hemp Seeds | 166 | 9.47 | 14.6 | 2.6 | 1.2 | Magnesium, Iron |
Sesame Seeds | 206 | 6 | 18 | 8 | 4 | Calcium, Iron |
You see that seeds give you a good amount of plant-based protein and fiber. Chia seeds stand out for their high fiber and calcium. Hemp seeds offer more protein than most other seeds. Pumpkin seeds supply magnesium and iron, which help your muscles and blood. Sunflower and sesame seeds provide healthy fats and minerals.
Tip: You can mix different seeds to get a wider range of nutrition in your meals.
Seeds also contain vitamins like vitamin E, which protects your cells. You find omega-3 fatty acids in flaxseeds and chia seeds. These healthy fats help your heart and brain. The chart below shows how protein, fat, carbs, and fiber compare in different seeds:
Health Benefits
Seeds offer unique health benefits that support your body in many ways. You get more than just nutrition when you eat seeds. Chia seeds help lower cholesterol and support your heart. Flaxseeds contain lignans, which may protect you from cancer. Hemp seeds give you protein and minerals that help your muscles and bones.
Pumpkin seeds help your body fight tiredness because they contain iron and magnesium. Sunflower seeds provide vitamin E, which keeps your skin healthy. Sesame seeds support bone health with their calcium content.
Here is a quick look at the nutritional benefits and health effects of some popular seeds:
Seed Type | Health Benefits | Nutritional Highlights |
|---|---|---|
Chia Seeds | May decrease cholesterol, promote cardiovascular health | 8g fiber per 2 tbsp, omega-3 fatty acids, calcium, magnesium |
Flaxseeds | May protect against cancer, support heart health | Antioxidants, phosphorus, magnesium |
Hemp Seeds | Support muscle growth, provide minerals for bone health | High protein, potassium, magnesium, iron |
Pumpkin Seeds | Help fight tiredness, support immune system | Magnesium, iron, zinc |
Sunflower Seeds | Protect skin, support cell health | Vitamin E, healthy fats |
Sesame Seeds | Support bone health, help lower blood pressure | Calcium, iron, magnesium |
You can add seeds to salads, yogurt, or smoothies to get more nutrition. Seeds help you feel full and give you energy for your day. When you eat seeds, you support your heart, bones, and immune system. You also get plant-based protein that helps your muscles grow.
Note: Eating a variety of seeds gives you the best nutrition and health benefits.
Seeds are easy to add to your meals. You can sprinkle them on breakfast foods or use them in baking. Try different seeds to find the flavors and nutrition that work best for you.
Seed Varieties
Chia Seeds
You can find chia seeds in many supermarkets. These tiny seeds have a mild, slightly nutty taste. Chia seeds give you high levels of omega-3 fatty acids, fiber, and protein. You also get antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals. Chia seeds help control blood sugar and keep you feeling full longer. The fiber in chia seeds improves digestion and may lower cholesterol.
Nutrient | Content Range |
|---|---|
Protein | 15% – 25% |
Fat | 30% – 33% |
Carbohydrates | 41% |
Dietary Fiber | 18% – 30% |
Chia seeds are a superior source of omega-3 fatty acids compared to flaxseed. Research shows that chia seeds may improve glucose tolerance and lower cholesterol.
Flaxseeds
Flaxseeds taste mild and nutty. You get polyunsaturated fat, omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and magnesium from flaxseeds. You need to grind flaxseeds to absorb their nutrients. Flaxseeds support heart health and digestion. The lignans in flaxseeds act as antioxidants and may help lower blood pressure.
Evidence Type | Description |
|---|---|
Lignans | Improve lipid metabolism and support heart health |
Soluble Fiber | Lowers cholesterol and blood pressure |
Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Fight inflammation and protect your heart |
Flaxseeds add bulk to stool and help relieve constipation. Eating flaxseeds may improve gut health and lower cholesterol.
Pumpkin Seeds
Pumpkin seeds have a crunchy texture and a mild flavor. You get protein, phytosterols, and many minerals from pumpkin seeds. These seeds contain zinc, magnesium, phosphorus, and vitamin E. Zinc supports male fertility, and magnesium helps your bones stay strong.
Potassium
Iron
Zinc
Copper
Magnesium
Selenium
Phosphorus
Pumpkin seeds may help improve sleep quality because they contain tryptophan, which converts to serotonin and melatonin.
Sunflower Seeds
Sunflower seeds taste mild and add crunch to your meals. You get polyunsaturated oil, vitamin E, and magnesium from sunflower seeds. These seeds help your brain and support immune function.
Vitamin E protects immune cells and helps produce antibodies.
Zinc supports healthy immune response.
Selenium reduces inflammation and protects your immune system.
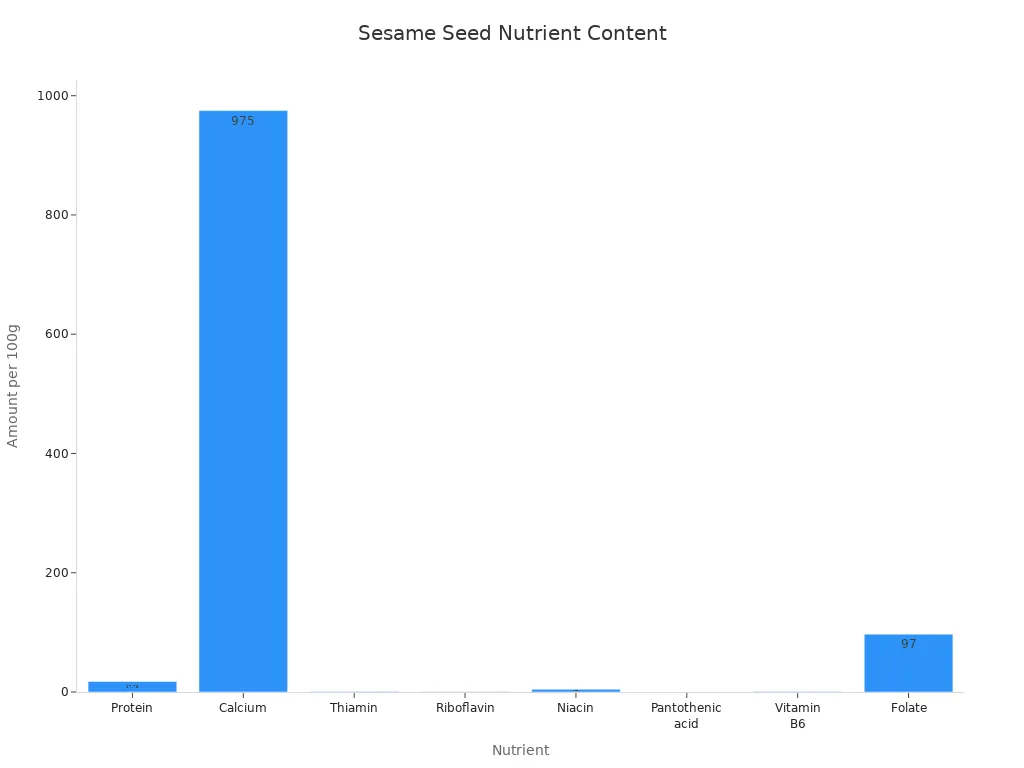
Sesame Seeds
Sesame seeds have a rich, nutty flavor. You get protein, calcium, and B vitamins from sesame seeds. These seeds also contain antioxidants and healthy fats. Sesame seeds may help prevent cardiovascular disease and cancer.
Nutrient | Amount per 100g |
|---|---|
Protein | 17.73 g |
Calcium | 975 mg |
Thiamin | 0.791 mg |
Vitamin B6 | 0.790 mg |
Vitamin E | Present |
Sesame seeds contain lignans and sesamin, which have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
Hemp Seeds
Hemp seeds taste mild and slightly nutty. You get plant-based protein, omega-3 fatty acids, and gamma-linolenic acid (GLA) from hemp seeds. These seeds support heart health and may reduce inflammation. Hemp seeds contain arginine, which helps relax blood vessels and lower blood pressure.
Hemp seeds may help lower inflammation and support metabolic health. You can add hemp seeds to smoothies, salads, or yogurt for extra nutrition.
Healthiest Seeds
Top Picks
You can find many seeds that support your health, but some stand out for their nutrient density and proven benefits. When you look for the healthiest seeds, you want options that give you protein, fiber, and healthy fats. Chia seeds, flaxseeds, and pumpkin seeds rank among the top choices.
Here is a table that compares the nutrition in chia seeds with other seeds and cereals:
Nutrient | Chia Seeds (per 100g) | Comparison with Other Seeds/Cereals |
|---|---|---|
Protein | 15-23% | Higher than wheat, oats, barley |
Dietary Fiber | 30-34g | Higher than quinoa (7g), flaxseed (27.3g) |
Omega-3 Fatty Acids | 64% | 10-fold higher than quinoa (6.7%) |
Total Fat | 25-40% | High in PUFAs (83%) |
Gluten-Free | Yes | Recommended for celiac disease |
Chia seeds give you more omega-3 fatty acids than most other seeds. You also get a rich supply of essential amino acids and dietary fiber. These nutrients help your heart, brain, and digestion.
Flaxseeds also deserve a spot on your list of healthiest seeds. Studies show that flaxseed can lower total and LDL cholesterol. Flaxseed, not just its oil, may help reduce blood pressure. Pumpkin seeds provide magnesium, zinc, and protein, which support your muscles and immune system.
Tip: You can mix different seeds to get a wider range of nutrients and health benefits.
Here are the main reasons why these seeds are considered the healthiest seeds:
Rich source of omega-3 fatty acids, which improve immunity and prevent heart disease.
Contains essential amino acids that help your body function well.
High dietary fiber content helps you meet daily intake goals.
How to Use
You can add the healthiest seeds to your meals in many simple ways. These seeds work well in both sweet and savory dishes. Try these practical ideas to boost your nutrition every day:
Salads: Sprinkle chia seeds or flaxseeds on fruit or salad bowls. You increase fiber intake and help stabilize blood sugar.
Yogurt and Oatmeal: Mix chia seeds into Greek yogurt or oatmeal. You get a filling breakfast that satisfies sweet cravings and keeps you full longer.
Soups and Beverages: Use chia seeds as a thickener in soups. You can also add them to drinks for extra hydration and fiber.
Chia Seed Pudding: Soak chia seeds overnight in milk. Add honey and fruit for a healthy breakfast or snack.
Baked Goods: Incorporate chia seeds or flaxseeds into breads, cookies, and cakes. You boost fiber content and add crunch.
You can also roast pumpkin seeds and eat them as a snack. Add them to trail mixes or sprinkle them on top of roasted vegetables. When you use the healthiest seeds in your meals, you improve taste and texture while supporting your health.
Note: Start with small amounts and increase gradually. Your body will adjust to the extra fiber and nutrients.
You can experiment with different combinations to find flavors you enjoy. Seeds make it easy to upgrade your meals and reach your nutrition goals.
Culinary Uses

Breakfast Ideas
You can start your day by adding seeds to your breakfast. Seeds like chia and sunflower give you protein and fiber. They also contain Vitamin C, which helps your immune system. Try these ideas to boost your morning meal:
Sprinkle chia or flaxseeds on oatmeal or yogurt for extra fiber.
Mix sunflower or pumpkin seeds into smoothie bowls for crunch.
Make chia pudding by soaking chia seeds in milk overnight.
Add hemp seeds to pancakes or waffles for more protein.
Top toast with nut butter and a handful of seeds for energy.
Seeds help you feel full longer and support digestion. They also provide minerals like magnesium and potassium, which help regulate blood pressure.
Salads and Mains
You can use seeds to make salads and main dishes more exciting. Seeds add crunch, flavor, and nutrients. The table below shows how different seeds work in various dishes:
Dish Type | Seed Type | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
Salads | Pumpkin/Sunflower | Added crunch, healthy fats |
Stir-fries | Sesame/Sunflower | Extra texture, flavor |
Crusted Proteins | Crushed seeds | Crunchy crust for proteins |
Seeds in salads and mains give you omega-3 fatty acids, fiber, protein, vitamins, and minerals. These nutrients support your heart, aid digestion, and give you lasting energy.
Baking and Snacks
You can use seeds in baking and snacks to boost nutrition. Try these tips:
Add sesame, poppy, or flaxseeds to bread and muffin batters.
Mix seeds into granola or energy bars for a nutrient-dense snack.
Use ground flaxseeds or chia seeds as a flour substitute in baking.
Toast seeds before adding them to recipes for a richer flavor.
Sprinkle seeds on cookies or brownies for extra texture.
Seeds contain antioxidants, healthy fats, and minerals. They help manage weight, provide energy, and lower cholesterol.
Flavor and Texture Tips
Seeds change the taste and feel of your food. Flaxseed adds a nutty flavor and crunch to salads or baked goods. Chia seeds swell in liquid and create a unique, gel-like texture in puddings. Poppy seeds give a nutty taste and crunch, especially in lemon muffins. Caraway seeds add an anise flavor to soups and salads. Sunflower seeds bring a mild, rich taste and extra texture to many dishes.
Tip: Toast seeds lightly to bring out their best flavor and keep them fresh in an airtight container.
You can explore many ways to use culinary seeds in your kitchen. They make meals more interesting and nutritious.
Buying and Storing
Choosing Seeds
You want to pick seeds that match your needs and taste. Look for seeds that grow well in your area and fit your cooking style. You should check the quality and nutrition before buying. The table below shows what you need to think about when choosing edible seeds:
Factor | Description |
|---|---|
Personal Preferences | Choose seeds you and your family enjoy eating. |
Gardening Space and Resources | Pick seeds that fit your available space, whether you have a garden or just containers. |
Local Climate and Conditions | Select seeds that thrive in your local temperature and sunlight. |
Level of Gardening Experience | Beginners should start with easy seeds. Experienced gardeners can try more challenging varieties. |
Disease Resistance and Yield | Look for seeds that resist disease and give good harvests. |
Reputable Seed Companies | Buy from companies with strong reputations and good reviews. |
Organic or Non-GMO Options | Choose organic seeds to avoid chemicals and pesticides. |
Tip: Always read labels and reviews before buying seeds. This helps you get the best quality for your meals.
Storage Tips
You need to store seeds the right way to keep them fresh and full of nutrients. Seeds can lose flavor and spoil if you do not protect them from air, moisture, and heat.
Use airtight containers like glass jars or vacuum-sealed bags to block moisture and air.
Store seeds in a cool, dark place or in the refrigerator to prevent rancidity.
Label containers with the seed type and date to track freshness.
Place seeds in airtight containers to keep out air.
Keep seeds in a dark, cool spot or refrigerate for longer shelf life.
Check seeds often for off smells. Discard any seeds that smell rancid.
Note: Proper storage keeps seeds crunchy and tasty. It also helps you keep their nutrition for longer.
Preparation
You can prepare seeds in different ways to boost their nutrition and flavor. Simple methods like soaking, sprouting, and fermenting make seeds easier to digest and more nutritious. The table below explains how each method works:
Method | Description |
|---|---|
Activating | Soak seeds in warm salted water, then dry at low temperatures. This keeps nutrients and gives a crispy texture. |
Fermenting | Soak seeds longer to grow good bacteria. Use for probiotic drinks or baking starters. This improves flavor and digestibility. |
Soaking | Soak seeds to remove phytic acid. This helps your body absorb minerals and increases vitamin content. |
Reducing | Sprout seeds to lower harmful substances and boost health benefits. |
Combine raw seeds with warm water and sea salt. Soak for 7 to 24 hours.
Drain and rinse seeds. Eat them moist or dry them for storage.
Dry seeds by spreading on dehydrator racks or baking trays at low temperatures until crisp.
Tip: Preparing seeds before eating helps your body get more vitamins and minerals. Try soaking or sprouting seeds to make them easier to digest and tastier in recipes.
Seeds give you many health and cooking benefits. You get protein, fiber, and healthy fats in every serving. Eating seeds often can lower your risk of heart disease and help control blood sugar.
Seeds are rich in vitamins and minerals.
They help you feel full and support weight management.
Seeds can lower LDL cholesterol and improve heart health.
Nelson’s demonstration plots show how learning about new seeds can inspire others to try them.
You can start with one or two types of seeds. Add them to your meals and enjoy new flavors. Over time, explore more varieties for better health.
Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
High Fiber Content | Supports digestion and regularity |
Protein Source | Helps muscles grow and repair |
Micronutrient Rich | Supplies key vitamins and minerals |
Blood Sugar Regulation | Keeps energy steady |
Weight Management | Helps you feel full longer |
FAQ
What is the best way to eat seeds?
You can eat seeds raw, roasted, or ground. Sprinkle them on salads, yogurt, or oatmeal. Add them to smoothies or baked goods. Try different ways to find what you like best.
Do seeds need to be soaked before eating?
Soaking seeds can make them easier to digest. It also helps your body absorb more nutrients. You do not have to soak all seeds, but it works well for chia, flax, and pumpkin seeds.
Are seeds safe for people with nut allergies?
Most seeds are safe for people with nut allergies. Sunflower, pumpkin, and chia seeds are good choices. Always check labels for cross-contamination warnings. Ask your doctor if you have concerns.
How much seed should you eat each day?
You can start with 1–2 tablespoons of seeds daily. This amount gives you extra nutrients without too many calories. Increase slowly if you want more fiber or protein.
Can you cook with seeds?
Yes! You can bake seeds into bread, muffins, or cookies. Toast them for extra flavor. Use seeds as a crunchy topping for soups or casseroles. Seeds add taste and nutrition to many dishes.

