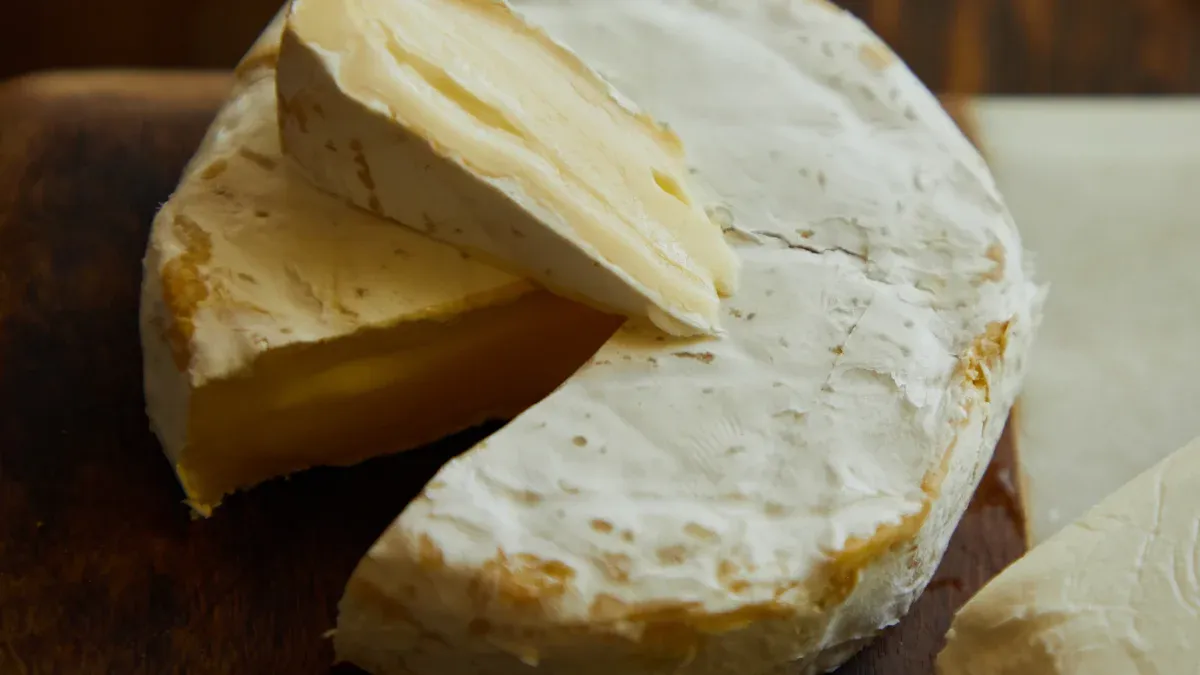

Brie is a soft cheese made from cow’s milk. You will notice its creamy texture and edible white rind. Brie comes from France and has become popular worldwide.
The popularity of brie has seen a notable increase in the United States over the past decade, driven by marketing efforts and consumer education about French cheeses. The cheese is so popular that it has a French museum dedicated to it.
If you wonder what is brie?, you will find its story and taste fascinating.
Key Takeaways
Brie cheese is a soft, creamy cheese with a mild, buttery flavor and an edible white rind. It is made from cow’s milk and has a rich history in France.
Enjoy brie at room temperature to enhance its creamy texture and flavor. Pair it with fruits like apples and pears, or serve it on a charcuterie board with meats and nuts.
Brie is nutritious, providing protein, calcium, and vitamins. Consume it in moderation to enjoy its health benefits while being mindful of calories and saturated fat.
What Is Brie?

Brie Cheese Overview
When you ask, “what is brie?”, you discover a cheese that stands out for its creamy and luxurious texture. Brie cheese is a soft and creamy cheese that comes from cow’s milk. You will often see it shaped in large wheels or rounds, covered with a white, edible rind. This rind forms from a special mold called Penicillium candidum, which gives brie cheese its unique look and taste.
You can recognize brie cheese by its pale yellow interior and its soft, gooey edge that becomes more pronounced as it ripens. The center stays a bit firmer, which creates a pleasant contrast in each bite. Brie cheese offers a mild, buttery flavor with hints of nuts. As it ages, the flavor grows stronger and more complex. Many people enjoy the light tones of cream and butter that make brie cheese so appealing.
Here is a table to help you see what makes brie cheese different from other cheeses:
Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
Texture | Soft and creamy, with a firmer consistency in the center. |
Flavor | Mild, buttery, with slightly nutty notes that become more pronounced with age. |
Rind | White, edible rind made from mold (Penicillium candidum). |
Milk Source | Traditionally made from cow’s milk. |
Interior Color | Pale yellow interior. |
You might wonder how brie cheese gets its special qualities. The process starts with cow’s milk. Cheesemakers add cultures and rennet to form curds. They then let the curds rest under conditions that help surface molds grow. Penicillium camemberti, a key mold, ripens the cheese and shapes its flavor. As brie cheese ages, the white mold changes the texture, making the outer layer gooey while the center stays chalky at first. Over time, minerals and enzymes move through the cheese, turning it into the soft, spreadable brie cheese you love.
Tip: If you want the best experience, let brie cheese sit at room temperature before serving. This brings out its full flavor and creamy texture.
Origin and Characteristics
When you explore what is brie?, you find a cheese with deep French roots. Brie cheese has been made in France for over a thousand years. A famous story tells how Charlemagne, the first king of the French, tasted brie cheese in the village of Meaux and liked it so much that he asked for it every year. Brie de Meaux, one of the most famous types, has been produced in northern France since the 8th century. People once called it the “Queen’s cheese,” and it earned special protection under French law in 1980.
France takes pride in its brie cheese. The country uses strict rules, called Appellation d’Origine Contrôlée (AOC), to protect the traditional ways of making brie cheese and to keep its link to the region. Over the centuries, brie cheese went from a local treat to a global favorite. In the Middle Ages, royalty enjoyed it, and at the 1815 Congress of Vienna, brie cheese earned the title “Prince of Cheeses.” Even as technology changed food production, brie cheese makers kept many old methods. Today, brie cheese holds a Protected Designation of Origin (PDO) status, which means only certain cheeses can use the name if they follow strict rules.
You can now find brie cheese made in many countries, but the French versions remain the most famous. Some popular types you might see include:
Brie de Meaux
Brie de Melun
Moses Sleeper
Thistle
Pianoforte
High Law Queen
Green Hill
Little Bloom on the Prairie
When you taste brie cheese, you enjoy a piece of history and tradition. Each bite connects you to the French countryside and the centuries-old craft of cheese making. If you ever wondered, “what is brie?”, you now know it is more than just a cheese. It is a symbol of French culture, a favorite around the world, and a delicious treat for any cheese lover.
Brie Flavor and Nutrition
Flavor Profile
When you taste brie, you experience a cheese with a mild, buttery flavor that feels rich and smooth on your tongue. The flavor profile of brie stands out because it combines several unique notes. You notice a creamy texture that almost melts in your mouth. This soft cheese often feels scoopable, making it easy to spread on bread or crackers.
Cheese experts describe the flavor of brie as a blend of fresh dairy, subtle nuttiness, and a hint of mushroom. The edible rind adds a touch of umami and sometimes a light, vegetal flavor. Near the rind, you might taste a slight tang or saltiness, which gives the cheese more complexity. As brie ages, the flavor grows stronger, and the rind’s mushroomy notes become more pronounced.
Here is a table that shows the most common flavor notes you will find in brie:
Flavor Note | Description |
|---|---|
Creaminess | Wildly creamy, easy to scoop without a knife. |
Fresh Dairy Notes | Tastes like fresh milk, adding to the overall flavor. |
Mushroomy Qualities | The rind brings umami and mushroom flavors, especially in aged brie. |
Nuttiness | A subtle nutty flavor makes brie feel almost dessert-like. |
Vegetal Flavor | Some brie has a light, green flavor that pairs well with spring produce. |
Salty and Tangy | Near the rind, you taste a slight saltiness and tang, which adds depth. |
Tip: If you want the best flavor, let brie sit at room temperature for about 30 minutes before serving. This brings out its creamy texture and full flavor.
You can enjoy brie on a charcuterie board, where its flavor pairs well with fruits, nuts, and cured meats. The soft cheese also works well in baked dishes, where the creamy texture becomes even more pronounced.
Nutrition Facts
Brie is a nutrient-rich dairy product that offers both taste and nutrition. When you eat a 1-ounce (28-gram) serving of brie, you get a mix of calories, protein, and fat. Here is a quick look at the nutrition facts for brie:
Calories: 95–100 per ounce
Protein: 4–5 grams per ounce
Total fat: 7–9 grams per ounce
Saturated fat: 4–5 grams per ounce
You can see these values in the table below:
Nutrient | Amount per 1 oz (28g) |
|---|---|
Calories | 100 |
Protein | 4 grams |
Total Fat | 9 grams |
Saturated Fat | 4 grams |
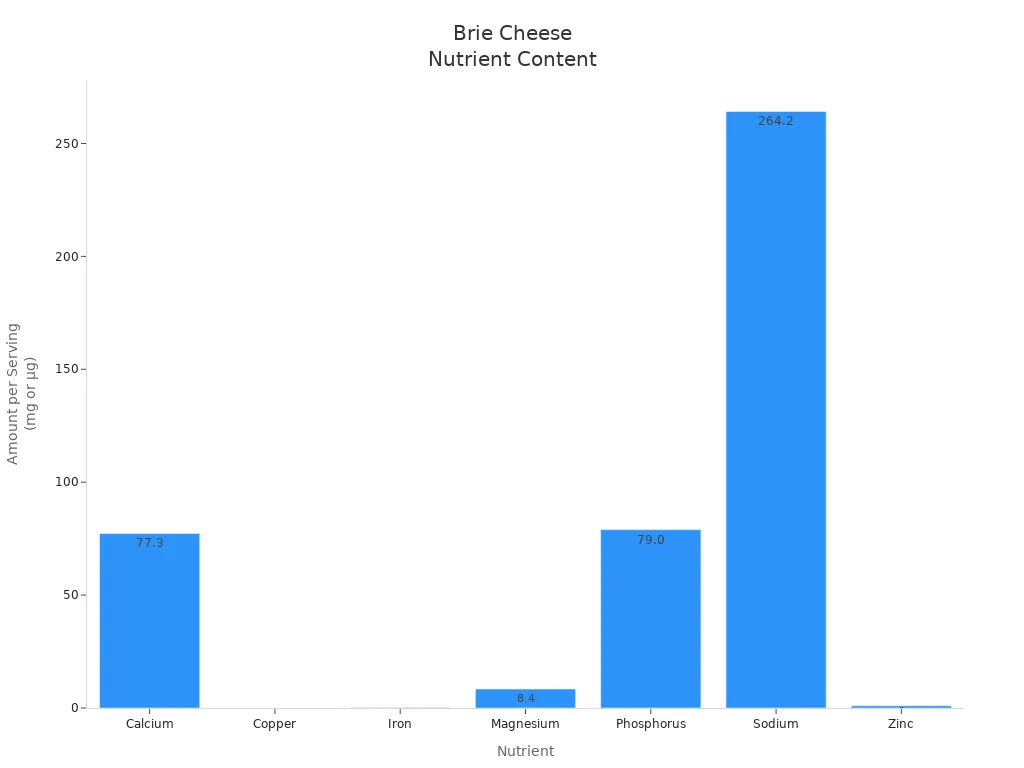
Brie also contains important vitamins and minerals. You get calcium, which helps build strong bones, and vitamin B12, which supports brain health and energy. The cheese also provides zinc, phosphorus, and magnesium. Here is a table showing the nutrients you find in a serving of brie:
Nutrient | Quantity per Serving | % Daily Value |
|---|---|---|
Calcium | 77.3 mg | 6% DV |
Copper | 8.0 μg | 1% DV |
Iron | 0.2 mg | 1% DV |
Magnesium | 8.4 mg | 2% DV |
Phosphorus | 79.0 mg | 6% DV |
Sodium | 264.2 mg | 11% DV |
Zinc | 1.0 mg | 9% DV |
Vitamin B12 | — | 29% DV |
Brie is a soft cheese that gives you a good source of protein and healthy fats. You also get health benefits from the probiotics found in brie, which can help your digestive system. The calcium and phosphorus in brie support bone health, while vitamin B12 helps your brain and energy levels.
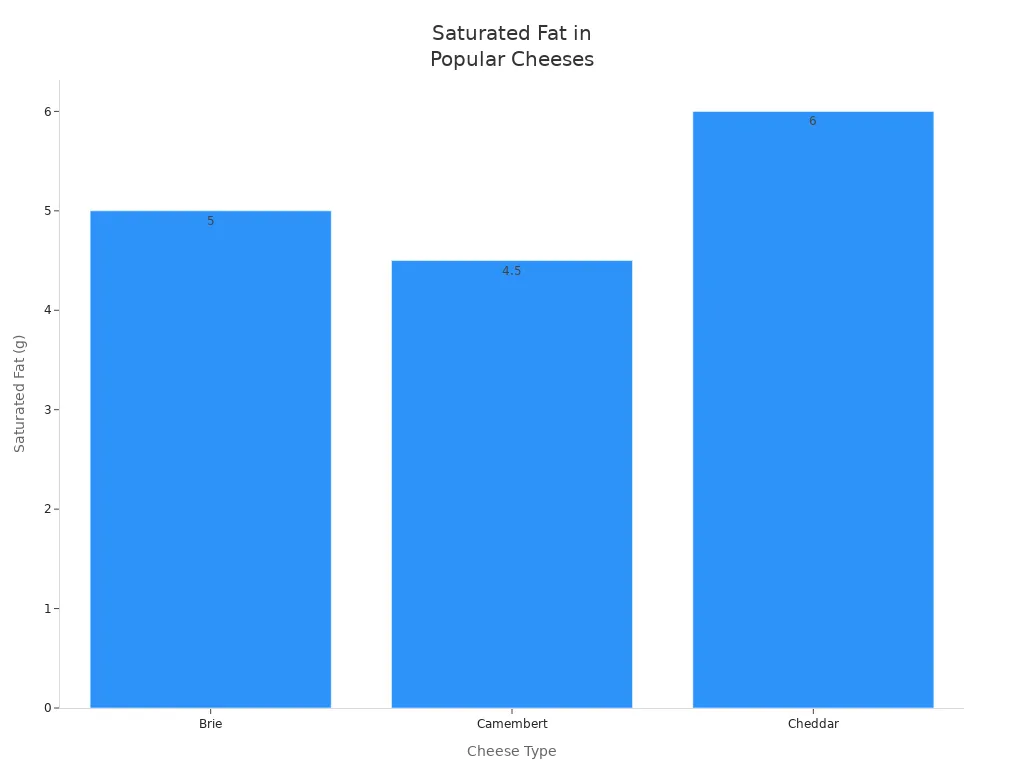
When you compare brie to other cheeses, you see that it has a moderate amount of saturated fat. For example, cheddar cheese has more calories and saturated fat per serving. Here is a table that compares brie with other popular cheeses:
Cheese | Serving Size | Calories | Total Fat | Saturated Fat | Protein | Sodium | Calcium |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Brie | 1 oz. | 94.5 | 8g | 5g | 6g | 178.5mg | 52mg |
Camembert | 1 oz. | 85 | 7g | 4.5g | 5.5g | 238.5mg | 110mg |
Cheddar | 1 oz. | 114 | 9.5g | 6g | 7g | 176mg | 204.5mg |
You should remember a few things when consuming brie cheese. Brie is high in calories and saturated fat, so eating too much can raise your cholesterol and increase the risk of heart disease. If you have lactose intolerance or a dairy allergy, you may experience discomfort or allergic reactions. Brie is a nutrient-rich dairy product, but you need to store it properly to avoid harmful bacteria like Listeria. Pregnant women and people with weak immune systems should be extra careful.
Despite these concerns, brie offers health benefits when you eat it in moderation. The cheese supports bone health, helps your digestive system, and provides important vitamins and minerals. You can enjoy brie as part of a balanced diet, especially when you add it to a charcuterie board with fruits and nuts.
Note: If you want to get the most health benefits from brie, eat it in small amounts and pair it with fresh foods on your charcuterie board.
Ways to Enjoy Brie
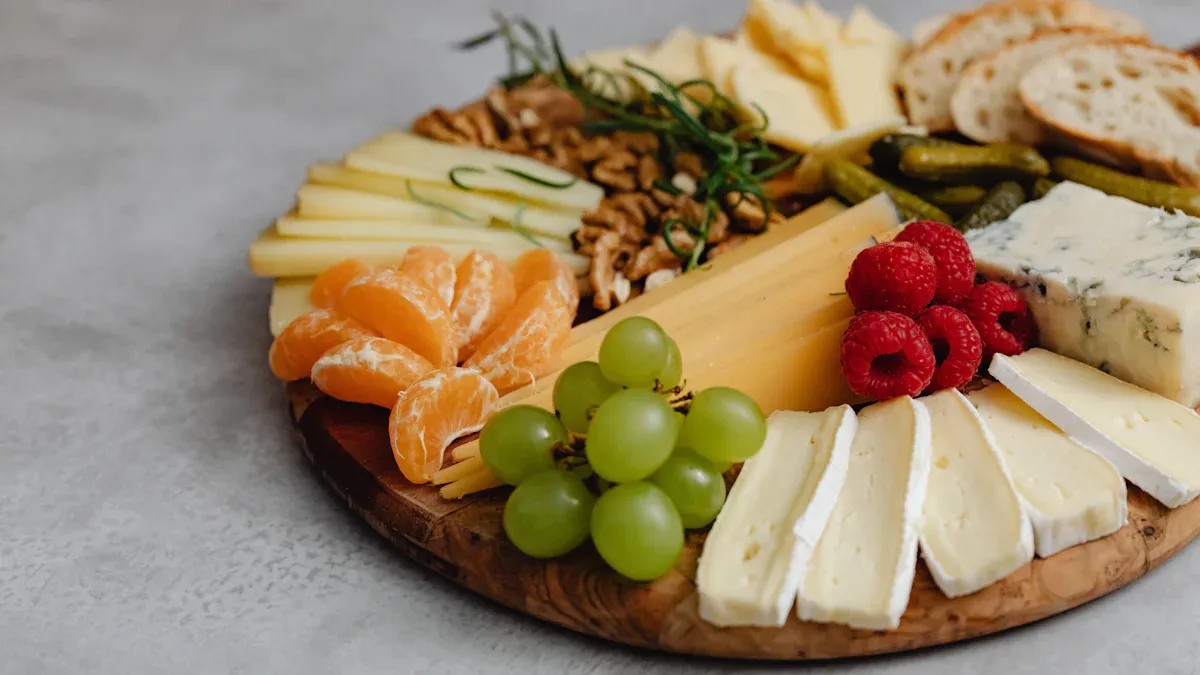

Serving Ideas
You can find many ways to enjoy brie at home or at gatherings. Brie shines on a charcuterie board, where its creamy flavor brings balance to meats and fruits. Try serving brie with apples, pears, or grapes for a sweet and creamy contrast. Crusty bread, sliced baguette, or crackers add crunch and help balance the soft texture. For a warm appetizer, baked brie with honey or cranberry sauce offers a sweet and savory flavor. You can also try honey nut baked brie for a crunchy twist. Add nuts like almonds or pecans for extra texture and contrast.
Tip: Serve brie at room temperature to unlock its full flavor and creamy benefits.
Pairings
Brie pairs well with many foods and drinks. On a charcuterie board, include meats like salami or prosciutto for a savory contrast. Fresh dippables such as apple slices or cucumber rounds add balance and freshness. For successful flavor pairings, use the table below to see which fruits work best:
Fresh Cheese | Fruit Pairing | Flavor Notes |
|---|---|---|
Brie | Apples, Pears, Grapes | Sweet and creamy |
When selecting brie cheese for your board, consider wine pairings. Pinot Noir, Merlot, Champagne, unoaked Chardonnay, and Riesling all offer balance and contrast to brie’s rich flavor. These wines create complementary pairings and flavor balancing, enhancing the benefits of each bite.
Preparation Tips
For formal events, cut brie into different shapes for visual appeal. Garnish with fresh herbs, edible flowers, or citrus zest to add color and contrast. Store brie in its original packaging or cheese paper, then place it in an airtight container in the warmest part of your fridge. Enjoy within a few days for the best flavor and benefits. Try baked brie recipes like maple whiskey baked brie with walnuts or savory baked brie with pesto for new ways to enjoy brie. These dishes highlight contrasting flavors and textures, showing the benefits of flavor profile complementarity. Use these tips for optimizing brie pairings and create a charcuterie board that balances every bite with complementary foods and beverages.
Brie offers a creamy texture, mild flavor, and a rich French history.
You get calcium, protein, and vitamins from brie.
Brie works well on cheese boards or baked with fruit spreads.
Try brie with fresh baguette, apples, or jams.
Share your favorite brie pairings below!
FAQ
Can you eat the rind on Brie cheese?
Yes, you can eat the rind. The white rind is edible and adds a mild, earthy flavor to each bite.
How should you store Brie cheese at home?
Keep Brie in its original packaging or wrap it in wax paper. Place it in an airtight container and store it in the refrigerator.
What is the best way to serve Brie at a party?
Let Brie sit at room temperature for 30 minutes. Slice it and arrange with fruits, nuts, and crackers for a simple, attractive presentation.
